
In recent years, great progress has been made in relevant research, but there are still many defects, which seriously affect the sustainable and healthy development of ideological and political theory in colleges and universities. This paper takes the computerization and algorithm model of complex information network as the starting point, and the best method of science education and politics as the research standard. The document combines the principle of combining scientific and humanistic methods with the best method of university education knowledge and politics, provides the best method for the knowledge and political model of education, and analyzes the credibility. The empirical results show that the accuracy of the ideal model is 91%. The improved computerized model provides supporting data for stimulating the intellectual and political vitality of university theoretical courses, improving the educational effect, strengthening educational ideas and policies, and ensuring the quality of university education.
Taking great achievements, there are some problems in the current teaching policies of universities and colleges cannot be ignored: some “avant-garde” teachers one-sided understand the requirements of curriculum reform, blindly pursue the renovation of teaching forms, and simply understand the ideological and political activity curriculum as that students completely let go of self-study and discussion in the classroom [1,2]. However, it has not really been internalized into the students’ quality, and “the educational goal of students’ all-round development does not seem to have been really achieved”. In contrast, some teachers are not good at learning new ideas and stick to traditional teaching ideas and methods. In ideological and political teaching, teachers “write a book with a piece of chalk from beginning to end”, and students “draw in circles in class, read and recite before exams” are still common [3]. It has become an urgent need for teaching improvement in the context of curriculum reform to explore teaching strategies that match the requirements of core literacy training [4].
Of course, ideology and politics are simple. The process of the concepts and principles of politics and ideology reveals the most basic world laws, which are very universal in nature and contain simple beauty. Ideology and political education are certainly realities. According to the knowledge and political standards of university education, build morality, train successors of the socialist country, and achieve all-round moral, intellectual and physical development. To cultivate the basic ability through political identification, scientific spirit, legal awareness, public participation and other “necessary personal values and core force corrections gradually formed through theme research”[5]. On the other hand, intelligent computing provides traditional statistical analysis methods for complex information networks to ensure the depth of information in complex information networks. On the other hand, traditional research on complex information networks provides theoretical support for developing intelligent computing models and algorithms.
However, at present, most research on complex information networks focuses on the physical characteristics of networks or the special applications of complex information networks in a certain field, and few studies focus on the impact [6]. Without the technical support of intelligent computing models and algorithms, research on complex information networks cannot play a role in intelligent computing and intelligent services. From the perspective of complex information networks, the strong demand for intelligent computing models and algorithms is becoming increasingly prominent. Through the in-depth analysis of innovation and reform [7]. It is necessary to enrich educational theory and political theory, and enrich the research results of theoretical education construction and reform. The evaluation index system of this research is formulated according to the requirements of political and ideological reform and the characteristics of universities and colleges.This will help to correctly understand the direction of the education, find the diagnostic role of the overall education, find the difference between the actual education and the goal, and explore effective strategies to improve the educational effect [8]. It will provide practical tools for the improvement of scientific development, ideology and political education. The education director shall supervise the implementation of the teaching reform.
In short, evaluating the intellectual and political methods that are most suitable for universities and college education, as well as their impact on intelligent computing models, will help teachers understand the educational situation and students’ learning, and understand the gap with the reform goals. Therefore, this research will help managers and teachers to provide reliable reference through training, decision-making and training improvement.
In the domain of intelligent computing, complex networks play a significant role in multivariate parameter optimization. This section outlines the key characteristics of these networks under the optimization framework.
The local process for multivariate parameter optimization can be represented by the following equations:
\[\label{GrindEQ__1_} h_{lm} = \frac{\partial S(\theta^i)}{\partial \theta^l \partial \theta^m} \quad (i \leq l,m \leq d),\tag{1}\]
\[\label{GrindEQ__2_} \theta^{i+1} = \theta^i – H^{-1}(\theta^i) g(\theta^i),\tag{2}\] where \(H\) denotes the Hessian matrix, and \(g\) represents the gradient.
To enhance the training process, the backpropagation algorithm is utilized in conjunction with the Newton iteration method to implement the steepest descent minimization approach. This is formulated as:
\[\label{GrindEQ__3_} \begin{cases} w_{ij}^{(k+1)} = w_{ij}^{(k)} – \lambda^{(k)} \left(\frac{\partial E}{\partial w_{ij}}\right)^{(k)}, \\ \vartheta_i^{(k+1)} = \vartheta_i^{(k)} – \lambda^{(k)} \left(\frac{\partial E}{\partial \vartheta_i}\right)^{(k)}. \end{cases}\tag{3}\] Even in high-dimensional problems, this approach yields the optimal results, as demonstrated in:
\[\label{GrindEQ__4_} \lambda^{(k)} = \min\left\{\lambda_{w_{ij}}^{(k)}, \lambda_{\vartheta_i}^{(k)}\right\}.\tag{4}\] For the weight update equation:
\[\label{GrindEQ__5_} w_{ij}^{(k+1)} = w_{ij}^{(k)} – \lambda_{w_{ij}}^{(k)} \left(\frac{\partial E}{\partial w_{ij}}\right)^{(k)},\tag{5}\] the corresponding updates are obtained through:
\[\label{GrindEQ__6_} \Delta w_{ij}^{(k)} = w_{ij}^{(k)} – w_{ij}^{(k-1)},\tag{6}\]
\[\label{GrindEQ__7_} \Delta \hat{g}(w_{ij}^{(k)}) = \left(\frac{\partial E}{\partial w_{ij}}\right)^{(k)} – \left(\frac{\partial E}{\partial w_{ij}}\right)^{(k-1)},\tag{7}\]
\[\label{GrindEQ__8_} \lambda_{w_{ij}}^{(k)} = \frac{\Delta \hat{g}(w_{ij}^{(k)})^T \Delta w_{ij}^{(k)}}{\Delta \hat{g}(w_{ij}^{(k)})^T \Delta \hat{g}(w_{ij}^{(k)})}.\tag{8}\]
The training method leverages the principles of weighted naive Bayesian theory. The objective function can be expressed as follows:
\[\label{GrindEQ__9_} c(x_{i}) = \arg\max_{c_{i} \in \mathcal{Y}} P_{w}(c_{i}) \prod_{j=1}^{n} P_{w}(x_{ij} \mid c_{k}),\tag{9}\]
where \(P_{w}(c_{i})\) represents the weighted probability of class \(c_{i}\), and \(P_{w}(x_{ij} \mid c_{k})\) denotes the weighted conditional probability of feature \(x_{ij}\) given class \(c_{k}\).
Next, we perform spherical harmonic analysis, which is calculated using the following equations:
\[\label{GrindEQ__10_} a_{n,m} = \int_{0}^{2\pi} \int_{0}^{\pi} \sin(\theta) f(\theta, \varphi) \bar{Y}_{n}^{m}(\theta, \varphi) \, d\theta \, d\varphi,\tag{10}\]
\[\label{GrindEQ__11_} f(\theta, \varphi) = \sum_{n=0}^{\infty} \sum_{m=-n}^{n} a_{n,m} Y_{n}^{m}(\theta, \varphi) \quad (n > 0),\tag{11}\]
\[\label{GrindEQ__12_} Y_{n}^{m}(\theta, \varphi) = \sqrt{\frac{(2n+1)(n-m)!}{4\pi(n+m)!}} P_{n}^{m}(\cos(\theta)) e^{im\varphi},\tag{12}\] where \(Y_{n}^{m}(\theta, \varphi)\) represents the spherical harmonics, \(P_{n}^{m}(\cos(\theta))\) is the associated Legendre function, and \(f(\theta, \varphi)\) denotes the function being analyzed.
For three-dimensional discrete Fourier transformation, the computation is represented by the following equations:
\[\begin{aligned} \label{GrindEQ__13_} y_{u,v,w} = \frac{1}{N^{3}} \sum_{i=-\frac{N}{2}}^{\frac{N}{2}-1} \sum_{j=-\frac{N}{2}}^{\frac{N}{2}-1} \sum_{k=-\frac{N}{2}}^{\frac{N}{2}-1} x_{i,j,k} \cdot \times \exp\left(-j \frac{2\pi}{N} (iu + jv + kw)\right), \end{aligned}\tag{13}\]
\[\label{GrindEQ__14_} X = \left\{x_{i,j,k} \mid -\frac{N}{2} \le i,j,k \le \frac{N}{2} – 1\right\},\tag{14}\]
\[\label{GrindEQ__15_} Y = \left\{y_{u,v,w} \mid -\frac{N}{2} \le u,v,w \le \frac{N}{2} – 1\right\},\tag{15}\] where \(x_{i,j,k}\) represents the input data in the spatial domain, and \(y_{u,v,w}\) is the corresponding output in the frequency domain after the Fourier transformation.
From the perspective of the evaluation system, the practice of universities in improving knowledge and education policies—such as determining the direction and objectives of evaluation, selecting appropriate thematic evaluations, establishing a scientific indicator system, collecting relevant information, and monitoring the effective use of evaluation results—is essentially an isolated evaluation and a series of complex and systematic institutional arrangements. For the evaluation to be carried out smoothly, it requires support from other relevant systems, including cooperation between national legislation, the school personnel department, and the teacher salary system.
From the perspective of sustainable development, we should expedite the evaluation of legislation, further deepen the study of evaluation theory, improve the evaluation index system, and establish an external evaluation mechanism. If we only take the road of improving educational theory, then as a means and method, evaluation will become a source of strength. However, scientific evaluation cannot be guaranteed.
The main 10-year evaluation model based on network topology focuses on centralized evaluation over a 10-year period, considering the network structure and evaluating all years within the complex information network.
According to different theoretical characteristics, this paper will study the node correlation evaluation model, centrality and control evaluation model, heterogeneous fusion evaluation model, and other evaluation models under the local network topology. The relationship between the models is shown in Figure 1.

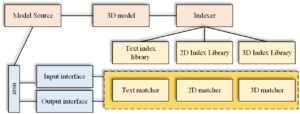
At the same time, complex networks use intelligent computing models and algorithms. According to complex network technology, research intelligent computing models and algorithms. For 3D model retrieval system, many models contain concave, and the non-uniqueness of extended Gaussian image on concave is a big defect, as shown in Figure 2.

A 3D model retrieval system shall include a 3D model database; A feature library extracted from each 3D model in the corresponding database; Program module for analyzing geometric features of user input model; The program module that searches and matches the extracted input model features in the 3D model feature library and the output module. The structure of a standard 3D model retrieval system is shown in Figure 3:
The real ideological and political value of education lies in encouraging students to form basic ideology and political characteristics through teacher education, and completing the basic task of moral education. It can be seen from the survey and statistics that students believe that in terms of ideology and politics, and the average income of “wisdom” is less than 25%. From the general curriculum of ideology and politics observed at present, education is still limited to knowledge education. Teachers often ignore students’ feelings, attitudes and values, which is inconsistent with the teaching content and process (16): \[\label{GrindEQ__16_} c\left(x_{i} \right)={\mathop{\arg \max }\limits_{c_{i} \in {\rm {\mathcal Y}}}} P_{w} \left(c_{i} \right)\prod _{j=1}^{n}P_{w} \left(x_{ij} c_{k} \right) .\tag{16}\] As shown in Figure 4, the adaptive atomization system is the best atomization system of the neural network, which is the same as the first command to draw a successful conclusion from the function.
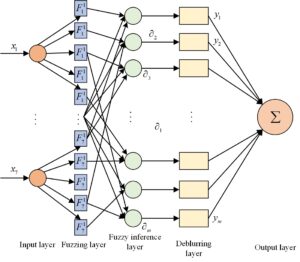
The first three layers correspond to the T-S fuzzy neural network precursor network, and the last two layers correspond to its successor network. The functions of each layer are optimized below, as shown in Figure 5.
The basic data of the structure which provides diversified student information, teacher information, curriculum information table, etc. As Table 1 for other data structures and index boundary database used by this subsystem to store various boundary value structures of evaluation criteria. The sample database is used to store all expert samples, including training samples and test samples. As Table 2 for the structure. The database of status is used to store the learning data (indicators rather than grades) of all students in a certain course. As Table 3 for the structure, the ideological and political learning evaluation grade database is used to store the student’s index grades and comprehensive evaluation results. As Table 4 for the structure.
| Field Name | type | width | Decimal Digits | remarks |
| indnum | character | 2 | Index No | |
| indname | character | 20 | Index name | |
| BJ1 | Numerical | 4 | 1 | Excellent and good boundary value |
| BJ2 | Numerical | 4 | 1 | Boundary value of good and medium |
| BJ3 | Numerical | 4 | 1 | Intermediate and pass boundary value |
| BJ4 | Numerical | 4 | 1 | Boundary value of pass and difference |
| Field Name | type | width | Decimal Digits | remarks |
| swnumber | character | 6 | Index No | |
| onlinetime | character | 4 | Indicator 1 Evaluation grade (online duration) | |
| execrate | character | 4 | Indicator 2 Evaluation grade (operation completion rate) | |
| soutime | character | 4 | Indicator 3 Evaluation grade (learning resource duration) | |
| prosum | character | 4 | Indicator 4 Evaluation grade (number of initiated questions) | |
| anssum | character | 4 | Indicator 5 Evaluation grade (number of questions answered) | |
| aveworkagr | character | 4 | Indicator 6 Evaluation grade (average operation score) | |
| avetestagr | character | 4 | Index evaluation grade 7 (average test score) | |
| evaluationagr | character | 4 | Comprehensive evaluation grade |
| Field Name | type | width | Decimal Digits | remarks |
| S_ NUM | character | 10 | Student ID | |
| C_ NUM | character | 4 | Course No | |
| S_ onlinetime | character | 4 | Indicator 1 Evaluation grade (learning duration) | |
| S_ exerate | character | 4 | Indicator 2 Evaluation grade (operation completion rate) | |
| S_ routine | character | 4 | Indicator 3 Evaluation grade (resource use duration) | |
| S_ prosum | character | 4 | Indicator 4 Evaluation grade (number of initiated questions) | |
| S_ assum | character | 4 | Indicator 5 Evaluation grade (number of questions answered) | |
| S_ aveworkagr | character | 4 | Indicator 6 Evaluation grade (average operation score) | |
| S_ avetestagr | character | 4 | Index evaluation grade 7 (average test score) |
| Field Name | type | width | Decimal Digits | remarks |
| S_ NUM | character | 10 | Student ID | |
| C_ NUM | character | 4 | Course No | |
| Ag_ onlinetime | character | 4 | Indicator 1 (learning duration) | |
| Ag_ execrate | character | 4 | Indicator 2 evaluation (operation completion rate) | |
| Ag_ soutime | character | 4 | Indicator 3 Evaluation (resource use duration) | |
| Ag_ prosum | character | 4 | Indicator 4 Evaluation (number of initiated questions) | |
| Ag_ assum | character | 4 | Indicator 5 evaluation (number of questions answered) | |
| Ag_ aveworkagr | character | 4 | Index 5 evaluation (average score of homework) | |
| Ag_ avetestagr | character | 4 | Index evaluation (average test score) | |
| Ag_ evaluationagr | character | 4 | Comprehensive evaluation grade |
In the absence of any test, it is excluded from the best way to educate daily thought and political life. At present, the improvement of educational ideology and political life is almost the same.
At present, China’s curriculum reform has entered the era of “basic quality”. The teaching quality must be implemented, and the evaluation work also needs to continue. At present, people have a highly consistent understanding of the importance of improving educational ideology and political courses. The research on evaluation principles, methods, standards and methods is still in the theoretical research stage, but there are still few strategies to improve the educational system in traditional and representative practice.
In short, the impact of education is the ultimate goal of education, which directly reflects the quality of education. From the above indicators. In particular, we have made remarkable achievements in education in terms of ideology, morality, political values and training quality.
Universities and colleges should cultivate theoretical thinking ability and scientific research ability, master knowledge and theory, and strengthen and improve the guidance from theory to practice. This article (WHO) believes that this is because junior colleges are not enough to study ideology and political theory and have invested more professional knowledge in vocational curriculum research. Educational theories and policies also ignore students’ research and theoretical thinking ability. The algorithm performance is tested with 20 groups of comprehensive data. The test results of the datasets listed in Table 5.
| data set | example | attribute | class | defect | Numerical |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| anneal | 899 | 38 | 7 | yes | yes |
| anneal. ORIG | 899 | 38 | 7 | yes | yes |
| balance-scale | 626 | 6 | 4 | yes | yes |
| breast-cancer | 287 | 11 | 3 | yes | no |
| breast-w | 699 | 211 | 3 | yes | no |
| colic, ORIG | 369 | 29 | 3 | yes | yes |
| credit-a | 691 | 17 | 3 | no | yes |
| credit-g | 1000 | 22 | 3 | no | yes |
| diabetes | 769 | 9 | 3 | yes | yes |
| heart-c | 304 | 15 | 6 | yes | yes |
| heart-h | 295 | 15 | 6 | no | yes |
| heart-statlog | 271 | 15 | 3 | yes | yes |
| hepatitis | 156 | 21 | 3 | no | yes |
| Ionosphere | 352 | 36 | 3 | no | no |
| kr-vs-kp | 3197 | 38 | 3 | yes | yes |
| labor | 58 | 18 | 3 | no | yes |
| letter | 20000 | 18 | 26 | no | yes |
| lymph | 149 | 19 | 4 | no | yes |
| segment | 2311 | 21 | 7 | no | yes |
Judging from the evaluation of teaching methods, classroom atmosphere and students’ feedback, teachers continue to use the undergraduate indoctrination teaching mode, and teachers speak, and students listen more generally. First, this will undoubtedly lead to students’ weariness of learning in the classroom and their learning attitude of muddling along with credit. The social background of college groups is complex, many of them have had social experience, and the indoctrination of theories will only disgust them. Moreover, colleges and universities are groups with certain learning ability and knowledge reserves and preaching alone cannot arouse learning interest. Such teaching content cannot meet their desire for knowledge. Therefore, data simulation is needed to judge the accuracy of the model.
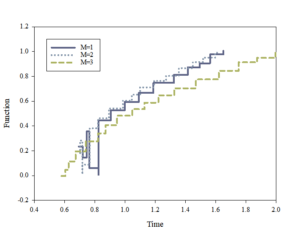
Ignoring your own university after teaching type teaching will directly reduce classroom interaction and student participation. Therefore, universities lack self-awareness and the appropriate atmosphere for speculative academic research in the classroom. This is in conflict with the teaching rules of the university. College is an independent group with learning and research capabilities. Only by mobilizing the initiative of learning and making it the theme of classroom teaching can we achieve this, can they effectively achieve the educational goal of cultivating their research ability and inquiry learning. Therefore, this outstanding problem needs to be improved. To solve this problem, this model performs noise reduction on two different data sets of ANFIS and BP network and uses the limited multi view mixed distribution as the optimization path. The experimental results are shown in Figure 6. The thick blue curve is the fitting result of the limited multi view mixed distribution, and the other five curves are the fitting curves of the single view distribution.
After model optimization, reliability and effectiveness are completed, it will be analyzed. As shown in Table 6, compare the test results of intersection B of neural network and neural network respiratory system. Comparing the data in Table 6, the results based model is better than the P-2 based on the resolution of about 5 percentage points.
| Model | Accuracy | Square absolute error | Root mean square error |
| Based on BP model | 78.1819% | 0.0983 | 02735 |
| Based on ANFIS model | 83.2728% | 0.0757 | 0.1575 |
As shown in Table 7, the evaluation model of neural network and artificial respiration test results shows that the neural network based on the training model is very accurate, but the accuracy rate is very low, only 68.5714%, far lower than the neural network model. On the one hand, few experts provide sample data, and the evaluation of ideology and political learning is not clear.
| Model | Accuracy | Square absolute error | Root mean square error |
| Based on BP model | 68.5715% | 0.1127 | 0.3033 |
| Based on ANFIS model | 91.4287% | 0.07 | 0.232 |
By comparing the simulation results, we find that the best method to evaluate educational knowledge and policies is not based on the neural network model, but based on the education and emotional thinking model. The emotional test of intelligence and political education shows that this is a high-precision evaluation model, which can improve the educational thought and political road by using emotion, and create a model to evaluate the educational effect. We also carried out further empirical verification of the model and conducted a random survey of 100 students. The result combination based on emotion is consistent with the expected assumptions in the questionnaire, as shown in Figures 7 and 8.


At present, the best theories and political methods in college education are still being explored. Considering the complexity of mathematics and the evaluation criteria of knowledge and political transfer in university education, this paper analyzes two improvement methods and improves the reliability and efficiency of the results. Experience shows that the best mental model is much better than neural network. The accuracy of the data obtained through the model test exceeds 91%, and the absolute error is less than 0.06, indicating that the model meets the expectations.
Scientific Research Project of Jilin Provincial Department of Education: Research on the Application of Blended Teaching in Ideological and Political Courses in Universities under the Background of Digital Technology – Taking the Course of “Outline of Modern Chinese History” as an Example, Number: JJKH20230005SZ
Research project of Jilin Higher Education Association::Research on the Integration and Development of Digital Technology and Ideological and Political Courses in Universities, Number: JGJX2023D534
Research project of Jilin Higher Education Association::Research on the Reform and Innovation of Ideological and Political Courses in Universities under the Background of Artificial Intelligence in the New Era, Number: JGJX2023D528.