
The ethnic minorities in the western region of China are widely distributed and have a large population, and have accumulated a large number of sports intangible cultural heritage with national characteristics. In order to protect the resources of intangible cultural heritage of sports in the western region and realize its sustainable inheritance, this study explored the protection of intangible cultural heritage of sports in the western region driven by information technology through the methods of literature review and interview. The research found that: information technology policy has created a good atmosphere for the transformation of intangible cultural heritage information to public behavior, information technology has realized the storage and management of massive intangible cultural heritage resources, and innovative information technology has realized the transformation of intangible cultural heritage information to the public. At the same time, the protection of information technology on the western sports intangible cultural heritage facing transmission distortion, the mass aesthetic fatigue, culture become a mere formality, lack of humanistic care, etc, so the future sports than genetic promise lasting sports intangible cultural heritage development plan, the reasonable injection “modernity” elements, fully predict sports non-material cultural heritage development trend and humanistic care is blended in among them.
he report of the 18th CPC National Congress emphasizes that cultural heritage carries the spirit, values and classical forms of national culture, and cultural heritage is the basis of cultural identity, cultural consensus and cultural creation, which can effectively drive the rapid development and prosperity of socialist culture [1,2]. General Secretary Xi Jinping has pointed out that the protection and inheritance of excellent traditional culture should not only emphasize the common development of social and economic benefits, but also reflect the important connotation of spiritual value [3]. The discussion of the CPC Central Committee on cultural value affirms the important position of sports intangible cultural heritage (hereinafter referred to as sports intangible cultural heritage) in social development, which has practical guiding significance for the research on the protection of sports intangible cultural heritage in western China [4,5].
According to the regional division, western China mainly includes 12 provinces and cities and autonomous regions, namely, five provinces and regions in southwest China (Chongqing, Sichuan, Yunnan, Guizhou and Tibet), five provinces and regions in northwest China (Shaanxi, Gansu, Qinghai, Xinjiang, Ningxia) and Inner Mongolia and Guangxi. It covers a total area of about 6.86 million square kilometers,accounting for about 72% of the total area of China [6,7]. The most important thing is that the ethnic minorities in western China are widely distributed, forming the sports intangible cultural heritage resources with ethnic characteristics, which exist in the form of skills or skills, and the sports intangible cultural heritage projects themselves have distinct characteristics of games, competitions and sports [8].However, under the impact of global commercial culture, the sports intangible cultural heritage that contains the national spirit is gradually fading out of the mainstream sports culture, and part or extinct, part or is on the verge of endangered [9], Show a significant marginalization, weak, non-mainstream trend. The sports intangible cultural heritage carried by the sports intangible cultural heritage may disappear in every minute and in every second, so it is urgent to strengthen the research on the protection and inheritance of the sports intangible cultural heritage in western China [10].
With the rapid development of high and new technology, information technology has been widely used in the development of the Internet of Things, intelligent vehicles, robots, modern production lines and other industries. At the present stage, the development of culture has become an important part of the core competitiveness of all countries in the world, and information technology is an inexhaustible driving force to promote cultural development. The integrated development of information technology and culture will become a new trend of cultural development in the future. Information technology mainly refers to the sum of[11,12] technologies for the acquisition, processing, storage, transmission and use of computer, network, radio and television. The culture transformed by information technology is the culture of science and technology, which reacts on information technology and affects the development of politics and economy.
As an important component of the intangible cultural heritage, the inheritance carrier of the sports intangible cultural heritage is the human itself, while the physical skills and behavior skills are the main expression mode, and the spiritual creation and communication are the basic path of its creation and inheritance [13] . According to the Nanjing sports college President, doctoral supervisor Yang researcher as editor of the introduction to sports intangible cultural heritage points out:sports intangible cultural heritage refers to our nationalities in extensive folk sports, folk sports, traditional sports project process, such as the groups or individuals as an important part of cultural wealth with game, education and competitive sports skills and skills, and in the process of the implementation of these skills and skills, the use of all kinds of equipment, related physical manufacturing process and show the sum of the space place [14] .
In the final analysis, the main body and medium of sports non-genetic inheritance are thousands of people. Only when the people feel the essence and essence of the intangible cultural heritage can they effectively inherit the intangible cultural heritage of the intangible cultural heritage resources and realize the protection and continuation of the sports intangible cultural heritage in a real sense [15].The most important thing in this process is to find a conversion point that can connect the intangible heritage resources and the intangible heritage audience, The scattered, incomplete and massive intangible cultural heritage resources will be centrally displayed in front of the public. Information technology is becoming more and more mature in the contemporary society, showing the powerful information management and processing functions, and it is the best choice to realize the transformation of sports intangible cultural heritage to the public’s inheritance behavior [16]. Thus planning the information technology perspective of the western sports heritage protection ideas: first, based on information technology policy to create good intangible protection atmosphere, followed by the level of information technology to realize the intangible information management and storage, finally with the aid of innovative information technology to intangible show to people, to perceive the sports intangible cultural heritage connotation and value, consciously become the heritage of sports heritage.
This study through the network database, library resources, experts visit channels to collect the western region intangible protection of information technology application data, using literature, interview, theory with practice depth analysis of information technology in the western region sports heritage protection information transformation role, reflect on the problems existing in the western China sports heritage protection and improve, in order to provide a reference for the western region sports heritage protection.
Information technology has provided high-level technical support for the construction of sports intangible cultural heritage database, intangible cultural heritage website, digital museum and other cultural inheritance and exchange platforms in western China, breaking the situation of intangible cultural heritage protection caused by word of mouth [17] . The western region of China includes Tibet, Xinjiang, Qinghai, Gansu, Shaanxi, Ningxia, Inner Mongolia, Sichuan, Chongqing, Yunnan, Guizhou and Guangxi provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the Central Government. Intangible cultural Heritage websites and digital museums are widely used information means of intangible cultural heritage protection in the western region [18]. First of all, this study deeply investigated the construction of intangible cultural heritage websites and digital museums in western China, and systematically mastered the information level of sports intangible cultural heritage protection in western China.
Taking the entrance of China Intangible Cultural Heritage Network · China Intangible Cultural Heritage Digital Museum as the entrance, the construction of provincial intangible cultural heritage websites in western China is shown in Table 1-3 (combined with literature data and statistics of China Intangible cultural Heritage network).
| Number | Area | Name of intangible cultural heritage website | Website of intangible cultural heritage website | Host unit |
| 1 | Shaanxi Province | Shaanxi Province intangible cultural heritage database | www.sxlib.org.cn | “National Cultural Information Resource Sharing Project” Shaanxi Provincial Branch Center |
| 2 | Nei Monggol | The Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region Intangible Cultural Heritage Protection Center | www.nmgfeiyi.cn | The Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region Material and Cultural Heritage Protection Center |
| 3 | Sichuan | Sichuan Provincial Intangible Cultural Heritage Protection Center | www.ichsichuan.cn | Sichuan Provincial Intangible Cultural Heritage Protection Center |
| 4 | Chongqing | Chongqing Intangible Cultural Heritage Protection Center | www.cqwhysyj.cn | Chongqing Cultural Research Institute |
| 5 | Yunnan | Yunnan Province Intangible cultural heritage protection network | www.ynich.cn | Yunnan Provincial Department of Culture and Tourism, Yunnan Provincial Intangible Cultural Heritage Protection Center |
| 6 | Guizhou | Guizhou Province Intangible cultural Heritage network | www.gzfwz.org.cn | Guizhou Provincial Department of Culture and Tourism, Guizhou Provincial Intangible Cultural Heritage Protection Center |
| 7 | Guangxi | Guangxi intangible cultural Heritage network | www.gxfybhw.cn | The Department of Culture and Tourism of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region and the Intangible Cultural Heritage Protection Center of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region |
| 8 | Xizang | Tibet’s intangible cultural heritage | www.chinatibetnews.com | China Tibet News Network, Tibet Autonomous Region Art Museum, Tibet Autonomous Region Intangible Cultural Heritage Protection Center |
| 9 | Xinjiang | Xinjiang tourism official website | wlt.xinjiang.gov.cn | The Culture and Tourism Department of the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region |
| 10 | Qinghai | The Qinghai Provincial Department of Culture and Tourism | whlyt.qinghai.gov.cn | The Qinghai Provincial Department of Culture and Tourism |
| 11 | Gansu | Gansu Provincial Department of Culture and Tourism | wlt.gansu.gov.cn | Gansu Provincial Department of Culture and Tourism |
| 12 | Ningxia | The Culture and Tourism Department of the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region | whhlyt.nx.gov.cn | The Culture and Tourism Department of the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region |
In Table 1, the intangible cultural heritage websites of Xinjiang, Qinghai, Gansu and Ningxia are jointly organized with the tourism networks of their regions, while other regions are independent intangible cultural heritage publicity websites.
| area | Level classification | Type of intangible cultural heritage project | Inheritance person information | policies and regulations | Related news | academic exchange | Number of information navigation functions |
| Shaanxi Province | \(\Delta \) | \(\Delta \) | \(\Delta \) | \(\Delta \) | – | – | Eight |
| Nei Monggol | – | \(\Delta \) | \(\Delta \) | \(\Delta \) | \(\Delta \) | \(\Delta \) | Ten |
| Sichuan | \(\Delta \) | – | \(\Delta \) | \(\Delta \) | – | – | Ten |
| Chongqing | \(\Delta \) | – | \(\Delta \) | \(\Delta \) | \(\Delta \) | \(\Delta \) | Ten |
| Yunnan | \(\Delta \) | – | \(\Delta \) | \(\Delta \) | \(\Delta \) | \(\Delta \) | 11 |
| Guizhou | \(\Delta \) | – | \(\Delta \) | \(\Delta \) | \(\Delta \) | \(\Delta \) | 13 |
| Guangxi | \(\Delta \) | \(\Delta \) | \(\Delta \) | \(\Delta \) | \(\Delta \) | \(\Delta \) | Ten |
| Xizang | \(\Delta \) | \(\Delta \) | \(\Delta \) | – | \(\Delta \) | – | Nine |
| Xinjiang | – | – | – | \(\Delta \) | \(\Delta \) | – | Six |
| Qinghai | – | – | – | \(\Delta \) | \(\Delta \) | – | Seven |
| Gansu | – | – | – | – | \(\Delta \) | – | Nine |
| Ningxia | – | – | – | – | \(\Delta \) | – | Eight |
Note: The \(\Delta\) symbol in the table indicates that this option exists, and the space indicates that this option does not exist.
As can be seen from Table 2, due to the joint establishment of intangible cultural heritage websites and tourism publicity websites in Xinjiang, Qinghai, Gansu and Ningxia, the publicity is smaller than independent websites in other western provinces. Overall, there are some problems such as poor type division of intangible cultural heritage projects, unclear information of inheritors, and imperfect description of policies and regulations.
| area | release time | Release content |
| 2022/11/2 | Announcement on the implementation of the “National Youth Non-genetic inheritors Support Program” | |
| Inner Mongolia 10 | – | – |
| 2022/11/1 | China has issued the Yellow River Protection Law to strengthen the protection, inheritance and promotion of the Yellow River culture | |
| Gansu 29 | 2022/11/2 | Provincial department of culture and tourism party group special study of the party’s twenty spirit |
| Guizhou 10 | 2022/10/21 | Lu Yongzheng introduced the study and discussion of the CPC Guizhou delegation and answered questions from reporters |
| 2022/10/19 | The party’s 20th Guizhou provincial delegation held a plenary meeting | |
| 2022/10/12 | Longlin intangible cultural heritage to welcome the bumper harvest | |
| Guangxi 4 | 2022/10/10 | Hezhou: Create a new business form of ïntangible cultural heritage +” to empower rural revitalization |
Table 3 statistics several intangible website release information frequently the latest news dynamics, Inner Mongolia, Gansu, Guizhou, Guangxi region intangible website information release more frequently: among them, Gansu intangible website only on October 1 to November 2 has updated article 29 news, as of November 4,2022, Inner Mongolia and Guizhou intangible website in October has updated 10 news information; because Guangxi intangible website released the following two news: longlin heritage to welcome harvest, Hezhou: create “intangible +” new formats, enabling rural revitalization.
Based on the above research results, we can see that the intangible cultural heritage website has been basically built in western China, which can transmit the relevant information about the protection of intangible cultural heritage normally, which is a good integration of information technology and intangible cultural heritage protection; however, the construction level of intangible cultural heritage website in western China is still uneven, and the information timeliness and functional construction of intangible cultural heritage websites in Xinjiang, Qinghai, Sichuan and Ningxia are relatively weak and need to be improved.
This study summarizes the construction of the intangible cultural Heritage digital museum in western China with the “Encyclopedia Museum Project”. The “Encyclopedia Museum Project” is a large-scale public science popularization project of Baidu Encyclopedia, which is a digital museum based on virtual reality technology and other scientific technologies. At present, the platform has 299 museums. According to the data of the “Encyclopedia Museum Plan” platform, the use of digital museums in western China is shown in Table 4 (according to the statistics of the “Encyclopedia Museum Plan” website).
| area | Shaanxi Province | Nei Monggol | Sichuan | Chongqing | Yunnan | Guizhou | Guangxi | Xizang | Xinjiang | Qinghai | Gansu | Ningxia |
| Number of digital museums | 15 | 1 Home | 15 | 1 Home | Three | Eight | Four | 0 | 0 | 0 | Two | 0 |
According to the data in Table 4, there are 15 online digital museums in Shaanxi province and Sichuan provinces, 8 in Guizhou province, Tibet, Xinjiang, Qinghai and Ningxia, and the number of online digital museums in other regions is lower than 5.
According to the in-depth investigation, the construction of digital museums in Shaanxi Province in western China is relatively perfect. In addition to the construction achievements in the “Encyclopedia Museum Plan”, Shaanxi Province has also established an independent “Shaanxi Digital Museum”. In 2012, the Shaanxi Provincial Government launched the construction of the “Shaanxi Digital Museum”, striving to build a digital professional platform for displaying cultural relics and intangible cultural heritage. Shaanxi Digital Museum has five modules: “Virtual reality museum, digital thematic exhibition, temporary exhibition and exchange exhibition, appreciation of fine cultural relics, forum and explanation”, which not only has the function of virtual reality embodiment, but also provide a special platform for explanation and opinion exchange.
Based on the above research results, it can be seen that the “Encyclopedia Museum Plan” of Tibet, Xinjiang, Qinghai and Ningxia in western China are all blank, and the construction of intangible cultural heritage digital museums is relatively scarce.
Intangible project protection is the remedy and reduction of our country one thousand history, is an important part of the socialist culture development in our country, however, due to the lack of supervision mechanism, the actual intangible protection work, local government often declare is give priority to, protection, economic development is given priority to, the bad phenomenon of [19] .
Declaration is mainly adopted, and protection is secondary. Due to the local government failed to stand in the national development point of thinking, easy to ignore the intangible cultural protection work for the significance of cultural development for a long time, lead to leaders thought astray, only pay attention to the intangible project declaration, late intangible protection practice is difficult to implement, even appear only set up institutions, no full-time staff. The lack of responsibilities of local governments in the protection of intangible cultural heritage is particularly significant in the second and third batches of national intangible cultural heritage projects.
The development of intangible cultural heritage economy is the main priority, and cultural protection is the second.”Protection first, rescue first, rational utilization, inheritance and development” is the guideline for the protection of intangible cultural heritage in China, and this policy defines the function of intangible cultural heritage protection: not only to realize cultural protection, but also to develop the economy. In fact, during the implementation of the cultural protection function, local governments often pay more attention to the responsibility of economic interests than the responsibility of cultural protection. This is mainly because the performance assessment has formed a huge constraint on the local government, but the cultural assessment is not perfect, so the pursuit of economic growth has become the key value orientation of the local government.
The so-called transformation function of information technology is to effectively spread the intangible sports intangible cultural heritage to the public, make it realize the value and function of the intangible cultural heritage, awaken the consciousness, and actively learn the skills and techniques of the intangible cultural heritage and show them to others. This process realizes the protection and dissemination of the intangible cultural heritage in a real sense. Human history, civilization and culture are always protected and inherited with the help of the body, and the power of the people is huge. The destination of the effective inheritance of intangible cultural heritage is the public behavior. Only when the people practice the non-inheritance of sports can they achieve a long and continuous intangible culture. This section mainly studies how to use information technology to realize the transformation of sports intangible cultural heritage information to public behavior, and return to the destination of cultural inheritance.
As early as in 2005, the central general office of the State Council issued the State Council general office on strengthening the intangible cultural heritage protection work opinions, emphasize the intangible cultural heritage inheritance work should be integrated use of text, audio, video and other digital multimedia means, guarantee the authenticity of the intangible resources collection and comprehensive, further build archives and database. In 2007, Under the call of the national policy, The western region has actively responded to the call and made efforts in the field of intangible cultural heritage protection: The Tibet Autonomous Region has established a list of intangible cultural heritage covering 38 items, Involving folk literature, music and dance, traditional drama and other categories; Shaanxi province has released the first batch of intangible cultural heritage list, The number of projects is up to 145, Folk dance, traditional drama, folk art and competition are all among them; Chongqing has identified the first batch of 62 provincial intangible cultural heritage lists, It covers folk dance, folk art, traditional drama, acrobatics and competition and other projects (data from 2007 for the Protection of Intangible Cultural Heritage, Han Huili, Music for life, 2008(02):20-28.). It can be seen that the protection of intangible cultural heritage in China has become the focus of national cultural development more than a decade ago, but the level of inheritance technology is limited, and the policy has not achieved significant cultural inheritance effect in the early stage of its promulgation.
With informatization rapid development in the world, in July 2016, the general office of the central committee of the communist party of China and the State Council general office jointly issued by the national informatization development strategy outline, based on the new situation of the rapid development of information technology of the 2006-2020 national informatization development strategy to adjust optimization, informatization development in the next 10 years to guide and planning. In December of the same year, The State Council promulgated the “13th Five-Year Plan” National Informatization Plan “, which is expected to achieve phased results in the construction of” Digital China ” in 2020. China’s central government and local governments at all levels have issued a series of policies to promote the development of information technology, and information technology has been widely applied to the protection of sports intangible cultural heritage, accelerating the pace of non-genetic inheritance. In the national informatization development policy and heritage under the dual call of the protection policy, across the country by means of information technology for the genetic bearing activities, the promulgation of information technology policy for the intangible resources to public behavior conversion create a good atmosphere, the western provinces around the information technology for the diversified protection behavior attempt:
Guizhou province held in October 2013, the “Guizhou intangible digital protection project pilot project symposium”, the positive response to the national informatization development strategy, focusing on intangible project as the object to carry out the digital protection pilot work, intangible protection work content mainly includes information collection, data conversion, resource induction, finishing storage. Under the leadership of the Guizhou Provincial government, local governments and universities in the province actively use digital means to integrate sports intangible cultural heritage information, among which the intangible cultural heritage protection work in Guiyang has achieved remarkable results, and it is planned to achieve the goal of saving 100 intangible cultural heritage resources from 2017 to 2019.
Xinjiang uygur autonomous region intangible legislation protection earlier, in 2008,2010 successively promulgated the Xinjiang uygur autonomous region intangible cultural heritage protection regulations, the Xinjiang uygur autonomous region uygur wood regulations on the art protection, to build the heritage protection institutions, the genetic bearing talent training, intangible protection using special funds to form the legislative constraints, regulating the behavior of intangible heritage protection. In March 2016, Xinjiang Intangible Cultural Heritage Protection and Research Center officially opened the wechat official account of “Xinjiang Art Research Institute” (WeChat ID: xjyishuyanjiusuo), which regularly released the intangible cultural heritage information in Xinjiang. However, the information protection means of intangible cultural heritage in Xinjiang mainly stay at the level of image, audio and video. In addition to the construction of intangible cultural heritage protection website, the construction of digital museum and digital protection platform in Xinjiang is still blank, and the information level of intangible cultural heritage protection needs to be improved.
In response to the call of the national policy, Tibet promulgated the first local regulation on the protection of Tibet on the protection of the intangible cultural heritage —— the Measures for the Implementation of the Intangible Cultural Heritage Law of the People’s Republic of China. In 2018, the first digital cultural center platform ” Tibet Autonomous Region Digital Cultural Center Platform was completed, with the website located at www.xzzzqqyg.com, at the same time, opened a WeChat official account: Tibet Arts Museum; Tibet Autonomous Region Digital Cultural Center platform realizes public cultural sharing, which can not only release information and on-demand art resources, but also provide online activities and creation services.
From the central to the local governments, all governments and governments have supported the development of the information industry [20] through policies and regulations. Under the guidance of national policies, the western provinces have not only made policy responses to the protection of intangible cultural heritage, but also planned and deployed the collection, sorting and storage of intangible cultural heritage information resources, which is also the first step in the effective inheritance of intangible cultural heritage.
The application of information technology in intangible cultural heritage protection is relatively common. The intangible cultural heritage protection functions of basic information technology are as follows: Constructing intangible cultural heritage management files [11] based on text editing technology. Intangible cultural heritage management archives effectively solve the problems of storage and management of intangible cultural heritage resources. The field visited binyang cannon dragon section intangible management department, with the help of the local people and inheritance on field research, understand the information means application for the influence of the cannon dragon section inheritance, Guangxi binyang cannon dragon section in recent years to strengthen the protection of intangible information: 1. binyang established intangible cultural heritage investigation team, responsible for collecting intangible project clues and information, and published the binyang intangible cultural heritage census data assembly, is a reflection of intangible information resources integration.2. Attach importance to the protection of the gunlong inheritors, set up a special fund project to ensure the life needs of the sports non-genetic inheritors, and clear away the worries of the inheritors to carry forward the sports intangible cultural heritage at home.3. In 2016, Binyang County formulated a transformation and protection plan for the intangible cultural heritage of the Gunlong Festival, which involves the overall protection, annual stratified protection plan and program. With the help of sports non-genetic protection experts, cultural inheritance is carried out from a scientific perspective.4. At present, the protection of Binyang Artillery Dragon Festival adopts the comprehensive method of text, image, video and audio recording to obtain intangible cultural heritage information data, and record the development history and status of sports intangible cultural heritage.
With the help of the head of the cultural management department of the Gunlong Festival in Binyang County, the changes of the protection and inheritance subjects of the local Gunlong Festival in Binyang County from 2018 to 2019 were obtained, as shown in Table 5.
| Evaluation project | Change situation |
|---|---|
| Learn the inheritors of Zhalong craft | An increase of about 70% |
| The inheritor of learning the cannon dragon dance skills | An increase of about 75% |
| Learn about the inheritors of the tour color rack | An increase of about 60% |
| Young people who consciously participate in the gun Dragon Festival performance | About 2 times the increase |
| Cannon Dragon Festival culture protection of the employment of personnel | An increase of about 40% |
| Bachelor degree or above | An increase of about 30% |
Data show that in the past two years, both the inheritors of the intangible cultural heritage and the personnel involved in the protection of intangible cultural heritage resources have increased significantly, especially the proportion of the inheritors learning the traditional skills. In addition, the increase is about 40%, and the staff with bachelor degree or above has increased by three layers. In general, with the improvement of the protection information level of The Festival in Binyang County, the participation of local people in inheriting intangible cultural heritage has been improved, and the previous attitude has been changed from indifferent attitude to physical protective behavior, which reflects the value of the application of information technology.
In addition, the Binyang Gulong Festival has had a great impact on the local tourism industry since it was listed in 2006. But due to the influence of the outbreak of the new champions league, since 2020 failed to recover, so the data capture for 2013-2019 cannon dragon festival attract tourists and income, from Figure 1, in the 1st, in 2014,2016 binyang gun dragon section respectively declining trend of consumption and tourists, and in February 2019 cannon dragon save 440000 attract tourists, tourism total consumption of 234 million yuan, significant rebound (data from “Guangxi county economic network”). It can be seen that in recent years, Binyang County has used information technology to improve the ways and means of the protection of the Festival, and expanded the scale of people involved in cultural inheritance. Vir, tourists pass the intangible cultural heritage of the Festival to others, realizing non-genetic inheritance to a certain extent.
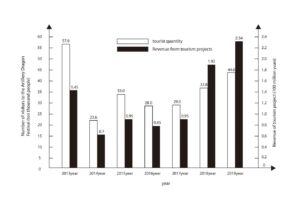
To sum up, with the application of information technology and the improvement of information protection level, the scale of the main body participating in the protection of Binyang Artillery Dragon Festival has expanded sharply in recent two years, and the non-genetic inheritance effect has been truly implemented.
Store intangible cultural heritage information based on video, audio and image sensors. In 2016, the census and filing and digital protection of non-genetic inheritors at the national and autonomous region levels in Tibet were basically completed, Store the intangible cultural heritage information in the form of images, audio and video, More than 100,000 intangible cultural heritage records, about 1,500 audio and video documents, and more than 40,000 intangible cultural heritage images (data from the “China National Radio Network · Xizang Channel”); In 2017, The Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region has planned the “rescue record of national representative inheritors of the Tajik Eagle dance”, During this activity, more than 1,000 intangible cultural heritage images were obtained, and the total amount of audio and video images reached 8TB, A large number of valuable intangible cultural heritage materials are stored (the data are from “The Exclusive Interview with Ge Yi, Director of The Research Center of Xinjiang Intangible Cultural Heritage Protection”).
Spread sports intangible cultural heritage information with the help of wechat and Weibo public platforms. Guizhou province, Yunnan province, Inner Mongolia autonomous region, Xinjiang uygur autonomous region, the Tibet autonomous region have launched the public platform, WeChat “Xinjiang art institute” WeChat ID for “xjyishuyanjiusuo”, “the Tibet autonomous region digital cultural center platform” WeChat public number name for “Tibet art museum”, Guizhou intangible WeChat public number for “Guizhou intangible cultural heritage”, the intangible information concentrated in the mobile digital carrier, more in line with the modern high frequency use mobile terminal way of life.
To understand WeChat public platform for the effect of intangible information protection and heritage, in Guizhou intangible WeChat cultural heritage platform of public effect research, research site for Guizhou university, on October 26,2019 in Guizhou university campus library randomly selected 50 students as research object, are willing to participate in the genetic research activities, the understanding, including eight people focus on “Guizhou intangible cultural heritage” WeChat public, so to the eight people detailed interview, interview object detailed information is as follows(as shown in Table 6):
| Student classification | Specific information |
|---|---|
| man student | Three people |
| woman student | Five people |
| The Department of Computer and Communications Engineering | One person |
| department of English | One person |
| Department of fine arts | Two people |
| Department of Journalism and Communication | One person |
| department of Chinese language and literature | One person |
| philosophy department | One person |
| Department of Public Administration | One person |
Through in-depth interviews with 8 respondents:
Student A (journalism department): “once in order to complete A press release on” Guizhou intangible cultural heritage ” WeChat public number, for the need of learning, before not very understand the intangible information, after reading a few articles found intangible cultural implication rich, profound, and a group of people to make up for the disappearance of ancient culture and positive efforts, worthy of admiration.” Student B (Chinese Department): ” Every time I update the article, I will read it carefully. The content is generally to release some dynamic information and notices of intangible cultural heritage research, etc. The update frequency is high, about two days, and the longest is generally no more than five days. I have learned a lot of intangible cultural heritage knowledge through the public account. For example, the state is implementing the “intangible cultural heritage poverty alleviation” policy, which is not only to help poor areas out of poverty, but also to centralized protection and inheritance of intangible cultural heritage.”
Student C (Department of Philosophy): ” I am more interested in intangible cultural heritage, so I pay more attention to the development of intangible cultural heritage. It is very convenient to understand the intangible cultural heritage information in the WeChat public account, and to timely understand the major events of the protection of the intangible cultural heritage. In daily life, I will recommend the intangible cultural heritage information to my classmates, and I will also participate in some offline intangible cultural heritage activities myself, so as to experience the intangible cultural heritage with a long history.”
Through field research, it is learned that the promotion form of wechat public platform is more suitable for young people’s living and learning style, and realizes the function of learning anytime and anywhere. Moreover, after the students of Guizhou University paid attention to the official account, they have changed from the original “no understanding” to the current “active learning” and changed their attitude towards the intangible cultural heritage; and the students will infiltrate the intangible cultural heritage into others in their life. Various phenomena show that the WeChat public platform plays a positive role in the dissemination of intangible cultural heritage, and can realize the transformation of the dissemination of intangible cultural heritage information to the human body.
The basic function of the database is to store and effectively manage the sports intangible cultural heritage information [12] . Its advantage lies in the conversion of text information, static pictures, dynamic video, audio files and other digital resources for storage, and initially realize the permanent and systematic storage of the intangible cultural heritage resources. In the information age, to integrate the western sports intangible cultural heritage resources, it is urgent to build the intangible cultural heritage protection database. The western provinces have carried out the practical activities of constructing the intangible cultural heritage database:
In Guizhou Province, on June 8,2017, Guiyang Culture, Press, Publication, Radio, Radio, Television and Television hosted the first “Cultural and Natural Heritage Day”, and awarded the “Guiyang Intangible Cultural Heritage Database” plaque to Guizhou Normal University University Science Park, and the construction project of “Guiyang Intangible Cultural Heritage Database” was officially launched. The establishment of the intangible cultural heritage database in Guiyang has realized the effective continuation of intangible cultural heritage resources; meanwhile, Guizhou University has launched the construction project of “Intangible Cultural Heritage Digital Resource Bank and Experience System” to actively build a comprehensive and comprehensive platform for the storage and sharing of sports intangible cultural heritage resources; in addition, the major bidding project of National Social Science Fund “Construction of Comprehensive Database of Tunpu Culture” is actively promoted with the help of Guizhou University.
Archives, museum of Yunnan province jointly build the minority cultural information resources directory, using the description of professional format of various types of intangible literature classification and indexing, through screening, classification, processing, indexing, description, digital processing steps, eventually form a digital form of literature information resources directory, namely the sports resources database. The database covers a large number of intangible cultural heritage resources, which truly realizes the efficient inheritance of intangible cultural heritage in Yunnan Province. In this study, the relevant officials of Yunnan Provincial Archives, interviewed the leaders of the intangible cultural heritage protection group and the personnel who have been engaged in the intangible cultural heritage protection work for many years, and learned about the advantages and disadvantages of the sports resource database in the sorting of intangible cultural heritage resources. The specific contents of the interview are as follows:
Person in charge: ” Data sorting at the beginning is manual copy records, and then conditionally used by computer records, but the classification of intangible cultural heritage information is not particularly clear, and the amount of data is huge, it is very inconvenient to find; and then little by little transition to form the current resource database. Database search information is particularly convenient and fast, and relevant content can be obtained by entering keywords; classified resources are stored with corresponding sports content stored in each directory; and these data are cleaned and filtered before inclusion in the database to eliminate invalid data.”
Staff: ” After the establishment of the resource database, it is particularly convenient for us to find information, and the work efficiency is significantly improved. We can put more time and energy on information collection and program formulation.”
Staff: ” After using the resource database, the information uncertainty was solved. In the past, the data resources were stored in the folder, but now the data is effectively collated, and the accuracy has been guaranteed.” According to the interview records, the application of the database plays a positive role in data collation, improves the convenience and efficiency, reduces the uncertainty of the use of intangible cultural heritage data resources, and ensures the accuracy of the dissemination of intangible cultural heritage resources.
Relying on the major projects of the National Social Science Fund of “research on the collation, inheritance and digital protection of Tibet’s intangible cultural heritage”, Tibet has improved the information level of non-genetic inheritance in Tibet. In 2016, Lhasa held the “intangible cultural heritage under the perspective of Tibetan culture protection and development” academic seminar, to build “Tibet intangible digital and database” plan, hope to build a collection of information collection, storage, display for the integration of the system platform, platform can unified management of intangible data and resource information, to standardization, systematic the genetic bearing management mechanism. This move has been effective on popularizing the characteristic culture of the Tibetan area and optimizing the scientific research level of the intangible cultural heritage.
Sichuan Province has established a digital protection platform for intangible cultural heritage. The expert seminar held on January 10,2018 made it clear that the digital protection platform of Sichuan intangible cultural heritage was built with “one database, one platform and four systems” as the core (data from ” Tencent Cloud https: / / cloud.tencent.com/developer/news/85248”).The construction of the digital protection platform for intangible cultural heritage in Sichuan Province has created the possibility for the protection and sharing of intangible cultural heritage data within the provincial level, and has set an example for other western provinces and cities to realize the informatization of intangible cultural heritage protection.
The object of virtual reality technology and digital museum is the audience of intangible cultural heritage communication, while the object of information sharing mechanism is the researcher of intangible cultural heritage protection. The three information technologies lead to the same destination, which act to transform intangible cultural heritage information into physical behavior.
Virtual reality technology (Virtual Reality, VR) builds a virtual three-dimensional world supported by computer graphics, 3D modeling, multimedia and other multi-disciplinary technologies, and realizes the realization of multi-source information fusion. Virtual reality technology can perform high-standard filtering repair and splicing [13] of the collected basic two-dimensional images, construct a visual three-dimensional model of the intangible cultural heritage, reproduce the dynamic and activation features of the intangible cultural heritage in a visual, auditory and tactile experience [14]. Meanwhile, virtual reality technology integrates human-computer interaction function, and the audience can not only watch, but also participate in it personally. Therefore, it is very necessary to introduce virtual reality technology in the process of non-genetic inheritance of sports. Virtual reality technology truly restores the form of the intangible cultural heritage, enables the audience to understand the connotation of the intangible cultural heritage, produce a sense of value identity, and then transform the value identity into the external physical inheritance behavior, and unconsciously transfer the intangible cultural heritage to others in life, so as to realize the inheritance of the sports intangible cultural heritage from generation to generation. It is important to note that virtual reality technology is not just watch, but to help the audience through the ornamental behavior understand intangible connotation and authenticity, the cold data into the audience enthusiasm inheritance behavior, in other words, virtual reality technology to public behavior information transformation of information technology expression, help people realize sports intangible cultural internalization.
This study has collected a large number of cases about the western provinces using virtual reality technology to innovate the intangible cultural heritage protection forms:
On August 2,2018, Guizhou Province held the “Qian · Vision 2018 Intangible Cultural Heritage and Art Week”, which uses modern technology to express the intangible cultural heritage, including the optical film and television museum, VR technology experience hall, photography and 3D illusion exhibition hall and other intangible cultural heritage exhibition methods. The intangible cultural heritage of the Art Week through virtual reality technology creates an immersive experience for the audience, adds interest to the boring cultural output, and enhances the interaction and communication of the intangible cultural heritage in a way to attract the curiosity of the masses (the materials are from the website of “Guizhou Culture headlines”).
In 2019, Guangxi Library held the “Cultural and Natural Heritage Day, a series of activities”, which mainly delivered the intangible cultural heritage of Guangxi and the traditional culture of Guangxi ethnic minorities to the audience in the form of virtual reality and cultural lectures. During the activity, the virtual reality technology meets the public as “black technology in the field of non-genetic inheritance”. After the experiencer wears the VR equipment, the open village and exquisite ethnic buildings are immediately presented immediately. Through the VR equipment, you can also experience the drum making process and ethnic ceremony performance process, and enrich people’s understanding of the intangible cultural heritage with the experience of virtual real experience.
Inner Mongolia Anda Culture and Media Co., Ltd., with the opportunity of the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, launched cultural and creative interactive products such as VR archery, VR aoobao, AR Mongolian clothing fitting room, breaking through the shackles of space, to show the traditional charm of culture to the audience, and the experiencer is like visiting the Mongolian grassland. In addition, the company has developed more than 100 interactive intangible cultural heritage products to convey the charm of intangible cultural heritage to the audience in schools, museums, shopping malls and other places. This move indicates that the use of virtual reality technology in the protection of intangible cultural heritage is no longer just an idea and an idea, and its effectiveness has been verified. The use of virtual reality technology to protect the intangible cultural heritage is a good way to enhance the interest and innovation of cultural inheritance. In addition, the School of Art of Inner Mongolia University has built a studio with digital choreography and sound driven technology. With the help of digital story choreography technology and storytelling technology, a virtual performance environment is built, giving the digital studio with the function of virtual music production and performance. The digital studio has created advanced performance conditions for Inner Mongolia sports intangible cultural heritage, and realized the continuation of the intangible cultural heritage in an information and innovative way.
Sichuan Province launched the intelligent service function for the first time at the exhibition “Non-genetic inheritance · Sichuan Practice” held in 2019, which also provided interactive exhibition experience with VR technology as the core, fully displaying the achievements of Sichuan intangible cultural heritage protection since the 19th CPC National Congress. Shaanxi silk road intangible culture co., LTD., in the digital technology heritage intangible make positive efforts, joint other technology companies actively build shaanxi province digital culture innovation platform, with VR, AR, AI and other high-tech means to present shaanxi intangible cultural achievements, rich genetic form, realize the intangible protection technology innovation and development.
Although the immersive experience of virtual reality technology captures the audience’s attention to the intangible cultural heritage from the perspective of curiosity, many practical activities affirm its positive role in the protection and inheritance of the intangible cultural heritage; virtual reality technology is the product of the current era and must play a positive role in the current era. Therefore, under the current background of social development, we should learn to make use of the advantages of virtual reality technology and give full play to its role of information transformation in the protection of intangible cultural heritage in western China, which is also the significance of virtual reality technology. Of course, each era has its own representative technology. With the improvement of science and technology level and the development of The Times, there must be a higher level and more powerful performance of technical means to replace virtual reality technology to better complete the protection and inheritance of intangible cultural heritage information, which will be the key direction of future research.
Virtual reality technology makes it possible for the integration of multi-source information in the protection of sports intangible cultural heritage. On the basis of virtual reality technology, the digital museum uses panoramic platform technology, computer network technology, 3D real scene technology and other comprehensive means to present the museum in the network carrier. Digital museum is an innovation in the form of intangible cultural heritage protection based on virtual reality technology: it takes the Internet to realize the information inheritance and storage of sports intangible cultural heritage through the intermediary, has the function of repairing the lost part of non-genetic inheritance, and makes real restoration through virtual reality technology. Digital museum is the trend and trend of obtaining intangible cultural heritage information in the information age. The way for users to use the virtual network museum is very simple. Just clicking the mouse to operate the computer can present the all-encompassing exhibition hall real [15] . Digital museums are relatively widely used in the protection of sports intangible cultural heritage in western China, and indeed play a role in the protection and inheritance of intangible cultural heritage information. Section 1.2 has explained in detail the application of digital museums in the protection of sports intangible cultural heritage in western China, which will not be repeated here.
Under the background of modern information technology innovation, large-scale data is generated in the process of sports intangible cultural heritage information collection. Based on these big data, using specific technologies for mining, decision-making and management can help researchers summarize the trend of intangible cultural heritage protection and predict the development trend, which is the advantage of big data technology. Sichuan Province introduced big data technology for the first time in the exhibition of “Non-genetic inheritance · Sichuan Practice”, and combined with a variety of information technology to jointly build the Sichuan intangible cultural heritage big data platform and smart intangible cultural heritage museum, and improve the audience viewing experience with mobile phone client application as the carrier. A special big data display window is set up at the exhibition site to dynamically disclose the information on the distribution, project protection and inheritance activity of intangible cultural heritage resources in Sichuan Province in the form of big data, so as to help the public understand the protection of intangible cultural heritage in Sichuan Province, so that the protection of intangible cultural heritage managers and inheritors can be supported. In addition, when designing the construction plan of Sichuan Province Digital Protection Platform for Intangible Cultural Heritage, Sichuan Province emphasized the importance of information technology such as the Internet, cloud computing and big data, and actively used big data technology to create a systematic, comprehensive and efficient intangible cultural heritage information protection environment. It can be seen that the practice of using big data for intangible cultural heritage protection in Sichuan Province has been promoted and achieved results, and its leading awareness of intangible cultural heritage protection is worth learning and reference in other western provinces.
Among them, the sports heritage information integration platform is a key link of accurate information sharing, need to do the following basic preparation: (1) clarify the internal structure and pedigree structure of the sports heritage protection project, clear the cultural characteristics of sports heritage; (2) sports heritage information data need to conform to the national data collection, conversion and other attribute standard . The information sharing mechanism of sports intangible cultural heritage based on big data technology is the idea of the integration of western sports intangible cultural heritage resources in the future, and it is an innovative practice of combining information technology and sports intangible cultural heritage protection. At present, the western region of China sports heritage protection and inheritance involves cultural management department, museum, intangible protection center, institute, limited to the system and technical obstacles, can only form an independent intangible protection situation, different departments repeated collection resources information, consume a lot of manpower and material resources. Therefore, accelerating the information sharing of intangible cultural heritage in western China is an effective way to maximize the benefits of intangible cultural heritage. Here, based on the big data information sharing mechanism of intangible information to public behavior conversion, the “people” refers to the field of different intangible research workers, information sharing mechanism provides researchers with data preservation and long-distance sharing function, effectively avoid the same data collection, improve the efficiency of intangible resources.
The original characteristics of sports intangible cultural heritage in western China are gradually fading and disappearing: 1. The inheritance of intangible cultural heritage lies in the real restoration of details and essence, driven by market demand, some inheritors pursue the number of non-genetic inheritance and ignore the cultural connotation of intangible cultural heritage, leading to the distortion of skills and the loss of cultural details.2. Although the achievements of sports intangible cultural heritage based on the transformation of information technology can optimize the efficiency of intangible cultural heritage protection, the loss of intangible cultural heritage data often occurs due to the defects of information technology itself, and the restoration of sports intangible cultural heritage is improper.3. Intangible cultural heritage is an important part of intangible cultural heritage, involving a wide variety of skills. The earliest inheritors who master the essence of intangible cultural heritage are gradually getting older and gradually lose the ability of non-genetic inheritance. The inheritors’ burnout of intangible cultural heritage protection leads to the lack of cultural culture.
All the above disorders can be summarized as “cultural distortion”. In view of the characteristics of marginalization and endangered of intangible cultural heritage in western China, it is necessary to formulate a long-term development plan of intangible cultural heritage and pay attention to the connotation protection of intangible cultural heritage. Only under the constraints of system and planning, can the restriction of objective factors on cultural inheritances be overcome. The long-term sports intangible cultural heritage development plan should adhere to the following points:
Formulate a targeted evaluation and feedback mechanism for sports intangible cultural heritage projects, conduct periodic evaluation and feedback on the development effect of intangible cultural heritage, and avoid the “cultural deficiency” [18] in each stage of intangible cultural heritage protection work.
Fine up the rules of the intangible cultural heritage market, strengthen the management of the intangible cultural heritage market, and completely eliminate the abnormal protection behaviors for the purpose of profit. Efforts should be made to improve the legislative protection of intangible cultural heritage projects, especially by adding targeted laws and regulations on traditional sports intangible cultural heritage projects, and to severely punish those who illegally destroy and destroy the protection work of intangible cultural heritage projects.
In the face of various uncertain factors of non-genetic inheritance, the integration of sports intangible cultural heritage protection and information technology is urgent, and the researchers and protectors of intangible cultural heritage need to constantly try to use information technology to restore the quality of intangible cultural heritage, expand the way of cultural communication, promote the historical value of sports intangible cultural heritage, and alleviate the distortion of sports intangible cultural heritage.
The intangible sports heritage contains certain national characteristics. For the performing sports non-genetic inheritance, the uniform performance content leads to public aesthetic fatigue. Moreover, modern culture and foreign culture have a huge impact on the traditional non-heritage. In order to avoid the public aesthetic fatigue, sports non-genetic inheritance must consider the innovation of cultural promotion and actively integrate the modern elements:
First of all, the innovation of sports intangible cultural heritage is not the blindly catering to the public’s unique aesthetic, but the innovation on the basis of guaranteeing the original flavor of the intangible cultural heritage, and integrating the fresh blood with national connotation and characteristics of The Times. Virtual reality technology and digital museum are both high-tech information dissemination means with the characteristics of today’s Times, which can highly restore the intangible cultural heritage skills and performance process, which is not only in line with the audience’s curiosity mentality, but also meets the principle of “real restoration” of intangible cultural heritage protection.
Secondly, rationally and scientifically inject “modern” elements into the intangible cultural heritage, which can fit the aesthetic standards of modern people and create a unique sports non-heritage industry. For example, the Artillery Dragon Festival in Binyang County: In ancient times, the Artillery Dragon Festival was mainly involved in young people. However, under the influence of diverse cultures, young people gradually lost the interest in inheriting the intangible cultural heritage. In view of this, the Binyang County government created opportunities to attract investment through the folk custom activities in the Festival, which injected certain economic development motivation for the inheritance and protection of the intangible cultural heritage of the Festival.
With the development of The Times, the level of information technology is updated repeatedly, and the popular elements of The Times are different. However, as the intangible cultural heritage protection workers, they should always combine the development level of The Times, inject vitality and “modern” elements into the intangible cultural heritage, and maintain the lasting vitality of the intangible cultural heritage.
Under the trend of globalization, western sports culture was introduced into China and quickly occupied part of the sports market, which became the main obstacle to the development of national sports in China. Young people’s character of seeking novelty, adventure and advocating challenges agree with western competitive sports, which makes national sports neglected. Moreover, there is a serious lack of value in the protection of sports intangible cultural heritage in western China, and many factors eventually lead to the non-genetic inheritance of sports in western China. Although dozens of colleges and universities in China have opened the traditional ethnic sports majors to cultivate the non-genetic inheritors of sports in the form of education, only the research of martial arts has an absolute advantage, and the research of other forms of sports is seriously ignored. The lack of penetration of sports intangible cultural heritage makes it difficult to highlight the core value of sports intangible cultural heritage.
Non-genetic inheritance is fundamentally formed because it is difficult to predict the implementation effect of a certain scheme, and the future protection behavior of non-cultural heritage is uncertain. In the era of high development of information technology, we should give full play to the role of big data technology in the protection and inheritance of intangible cultural heritage. Big data technology can clean, classify and transform the distributed and fragmented massive data, summarize the internal development law according to the current sports intangible cultural heritage protection data, and simulate and predict the future development trend, so as to guide the development direction of non-genetic sports in the future.
Information technology has the function of efficient collection and integration of data, but the rigid algorithm setting leads to the lack of emotional injection of intelligent science and technology, and the humanistic care in the process of information inheritance is often ignored. In western China, the older generation of non-genetic inheritors generally have the characteristics of old age, low educational level and poor physical condition, so in the use of information technology in sports non-genetic inheritors, we must pay attention to humanistic care:
First, attention should be paid to the protection of inheritors. Inheritors are the key nodes of sports non-genetic inheritance. Most of the intangible cultural heritage information data comes from the oral narration and is related to the personal experience of the inheritors. During the investigation of the intangible cultural heritage information, the researchers should pay attention to respect and cherish the inheritors, collect information under the condition of respecting the subjective ideas of the inheritors, and avoid providing false information due to the high language expression ability and physical condition of the inheritors, the information collectors should make reasonable work arrangements; focus on the inheritors of the intangible cultural heritage, it is difficult to live, the government needs to strongly support the protection and support policies of the intangible cultural heritage, and set up a special fund to guarantee the living expenses of the inheritors. For example, the inheritance of the Binyang Artillery Dragon Festival culture has achieved this point very well: the relevant departments have set up a special fund project to ensure the life needs of the sports non-genetic inheritors, so as to eliminate the inheritors’ worries about carrying forward the sports intangible cultural heritage culture.
Second, humanistic care means that economic interests should not be blindly pursued, and the productive protection of sports intangible cultural heritage needs to be true and reasonable. Local governments pursue the goal of economic growth, believing that the development of “intangible cultural heritage tourism production” can not only avoid the loss of intangible cultural heritage, but also stimulate consumption and drive economic growth, which can be regarded as a good way to develop GDP. This move is essentially a wrong interpretation and abuse of intangible cultural heritage protection methods. If information technology plays an excessive role in the function of productive intangible cultural heritage protection, it will cause the destruction and loss of sports intangible cultural heritage. Therefore, taking information technology as an opportunity to develop the protection of intangible sports heritage in western China, it is necessary to fully understand the core values of sports intangible cultural heritage and deeply interpret the core concepts of intangible cultural heritage; secondly, coordinate the relationship between economic growth and intangible cultural heritage protection with responsibility and rational thinking, take humanistic care as the starting point and foothold of productive protection of intangible cultural heritage, and create a sustainable protection road of intangible cultural heritage with characteristics of humanistic care under the joint efforts of all links.
The application of information technology in the protection of sports intangible cultural heritage is a prominent manifestation of the integration of modern science and technology and intangible cultural heritage. In general, the paper proves the effectiveness of the protection and inheritance of sports intangible cultural heritage in western China through scientific and technological means through the development examples of western China, and the information technology can realize the authenticity restoration and long-term storage of sports intangible cultural heritage. On this basis, the paper focuses on how information technology transforms intangible cultural heritage information into human body inheritance behavior, and clarifies the driving role of information technology in the protection of sports intangible cultural heritage in western China. The application of information technology is the main form and means for the protection of sports intangible cultural heritage in the future. Big data technology, artificial intelligence technology and cloud computing will become the key technical links for the long-term preservation of the intangible cultural heritage. Therefore, scholars and inheritors of intangible cultural heritage should explore their ideas, dare to try new technologies, timely correct and optimize the problems existing in the protection of sports intangible cultural heritage in western China, and strive to realize the complete inheritance and protection of sports intangible cultural heritage through information technology in the process of discovering and correcting mistakes.
There is no funding support for this study.