
NM-polynomial is commendably effective for computations of neighborhood degree sum based topological indices. This work comprises of computations of topological invariants which are first, second, third, fourth and fifth \(NDe\) indices, third version of Zagreb index, neighborhood second Zagreb index, neighborhood second modified Zagreb index, neighborhood forgotten topological index, neighborhood general Randi\’c index, neighborhood harmonic index, neighborhood inverse sum index, fourth atom bond connective index, fifth geometric arithmetic index, fifth arithmetic geometric index, fifth hyper first and second Zagreb index and Sunskurti index. In the end graphs are added for better understanding of these invariants.
hemical graph theory’s usefulness regarding the study of chemical and physical behaviour of different hydrocarbons is quite remarkable. Applied and computational mathematics has a very interesting field named chemical graph theory to study the structural activities of compounds [1]. Mathematical study of different symmetrical compounds such as hydrocarbons has gained more attention of pure and applied mathematicians [2] and [3].
Chemical graphs of organic compounds generally shows their molecular building structures which tends to have symmetrical behaviour. These graphs has strong predictions of their general biological and chemical processes and activities. Some physiochemical characteristics and topological invariants are applied to have better research results of chemical activities of organic hydrocarbons. NM-Polynomials and neighbourhood degree based topological invariants provide us information encapsulated in symmetrical structure without using any expensive lab experiments [4] and [5].
Graphs play a pivot role for the structural based physical, chemical and general properties of organic compounds. Any graph G describes the structure of compound with atoms as the vertices and chemical bonds of these atoms as the edges. Edge partition tables neighbourhood polynomials and neighbourhood degree sum based topological invariants completely represent any chemical graph G [6].
Topological invariants considerd as of more importance for the description of chemical graphs of organic hydrocarbons. These molecular descriptors are quite useful and effective with their number of acute applications in multiple fields namely mathematical chemistry, QSPR (Quantative Structure-Propertry relation) and QSAR (Qantitative structure-activity relation). Recently appreciable work has been done for detailed information, Reference available [7] and [2].
Molecular descriptor came into light when Wiener, the chemist discovered first topological invariant named as Wiener index. By this technique he was able to compare boiling points of different organic compounds. Differenet graphs of organic compounds are studied via NM-Polynomial [8],[9]. NM-Polynomials is based on the neighbourhood sum based degree of vertices connected by different edges. NM-Polynomials is used to formulate different toplogical indices recovered by various scientists and mathematicains. Hydrocarbons whose graphs are used in this work are based on Benzene rings known as Benzoid molecular graphs. These Benzoid systems are created in such a way that the two hexagons are either disjoint or having one or two common edges. Tetrameric 1-n adamantane is very important benzoid system as it is the basic unit of crude oil based products such as Petrol, diesel, kerosene oil and natural gas etc. Some important concept and topological invariant are given as follows
For a graph \(G\) a neighborhood degree based topological invariants is defined as: \[\label{eq:IG} NI(G) = \sum\limits_{xy \in E_{G}} f(\delta_{x},\delta_{y}).\tag{1}\]
By counting edges which have same end-degrees in the chemical graph then we can rewrite equation 1() as: \[\label{eq:IG2} NI(G) = \sum\limits_{j \leq k}m_{jk}f(j,k),\tag{2}\] where the relation \(\{\delta_{x},\delta_{y}\} = \{ j, k \}\) satisfied and \(m_{jk}\) is the total count of edges \(xy\) of the graph \(G\).
In 2021, S. Mondal et. al. introduced the \(ND\) indices [8] \[\begin{aligned} \text{First $ ND $ index}=&ND_1(G)=\sum\limits_{xy \in E_{G}} \sqrt{(\delta_{x})(\delta_{y})},\\ \text{Second $ ND $ index}=&ND_2(G)=\sum\limits_{xy \in E_{G}} \frac{1}{\sqrt{\delta_{x}+ \delta_{y}}},\\ \text{Third $ ND $ index}=&ND_3(G)=\sum\limits_{xy \in E_{G}} \delta_{x}\delta_{y}(\delta_{x} + \delta_{y}),\\ \text{Fourth $ ND $ index}=&ND_4(G)=\sum\limits_{xy \in E_{G}} \frac{1}{\sqrt{\delta_{x} \cdot \delta_{y}}}, \\ \text{Fifth $ ND $ index}=&ND_5(G)=\sum\limits_{xy \in E_{G}} \big[ \frac{\delta_{x}}{\delta_{y}} + \frac{\delta_{y}}{\delta_{x}} \big]. \end{aligned}\]
M. Ghorbani and M. A. Hosseinzadeh defined a third version of Zagreb index in 2013 [10].
\(M_{1}^{'}(G) = \sum\limits_{xy \in E_{G}}(\delta_{x} + \delta_{y}).\)
S. Mondal et al. introduced the neighborhood second Zagreb index in 2019 [11].
\(M_{2}^{\maltese}(G) = \sum\limits_{xy \in E_{G}}\delta_{x} \delta_{y}.\)
A. Verma and S. Mondal defined the neighborhood second modified Zagreb index in 2019 [6].
\(M_{2}^{nm}(G) = \sum\limits_{xy \in E_{G}}\frac{1}{\delta_{x} \delta_{y}}.\)
S. Mondal et. al. introduced the neighborhood forgotten topological index in 2019 [11].
\(F_{N}^{\maltese}(G) = \sum\limits_{xy \in E_{G}}(\delta_{x}^{2} + \delta_{y}^{2}).\)
A. Verma and S. Mondal defined the neighborhood general Randić index in 2019 [6]
\(NR_{\alpha}(G) = \sum\limits_{xy \in E_{G}}(\delta_{x} \delta_{y})^{\alpha}.\)
A. Verma and S. Mondal defined the neighborhood harmonic index in 2019 [6].
\(NH(G) = \sum\limits_{xy \in E_{G}}\frac{2}{\delta_{x} +\delta_{y}}.\)
A. Verma and S. Mondal defined the neighborhood inverse sum index in 2019 [6].
\(NI(G) = \sum\limits_{xy \in E_{G}}\frac{\delta_{x} \delta_{y}}{\delta_{x} +\delta_{y}}.\)
M. Ghorbani and M. A. Hosseinzadeh present in 2010 the fourth atom bond connectivity index as [12]:
\(ABC_{4}(G) = \sum\limits_{xy \in E_{G}}{\sqrt{\frac{\delta_{x} + \delta_{y}-2}{\delta_{x}\cdot \delta_{y}}}}.\)
Fifth geometric arithmetics index proposed by A. Grovac et. al. in 2011 and defined as [13]:
\(GA_{5}(G) = \sum\limits_{xy \in
E_{G}}\frac{2\sqrt{\delta_{x}\cdot \delta_{y}}}{\delta_{x}+
\delta_{y}}\).
V.R. Kulli introduced the fifth arithmetics geometric index in 2017 and defined as [14]
\(AG_{5}(G) =\sum\limits_{xy \in E_{G}} \frac{\delta_{x}+ \delta_{y}}{2\sqrt{\delta_{x}\cdot \delta_{y}}}\).
V.R.Kulli [15] proposed the fifth hyper first and second Zagreb index in 2017 and defined as:
\(HM_{1}G_{5}(G) = \sum\limits_{xy \in
E_{G}} \big( \delta_{x} + \delta_{y} \big)^{2}\),
\(HM_{2}G_{5}(G) = \sum\limits_{xy \in E_{G}}
\big( \delta_{x}\cdot \delta_{y} \big)^{2}\).
M. Hosamani proposed the sanskurti index in 2020 [7].
\(S(G) = \sum\limits_{xy \in E_{G}} \big(
\frac{\delta_{x} \delta_{y}}{\delta_{x} +\delta_{y} – 2}
\big)^{3}\)
A. Verma and S. Mondal defined the neighborhood M-polynomial in 2019 [16]: \[NM_{G}(u,v)=\sum\limits_{\psi \leq j \leq k \leq \Psi } m_{jk}u^{j}v^{k}. \label{eq:m}\] Here \(\psi = min \{d_{x}|x \in V_{G} \}\), \(\Psi = max \{ d_{x} | x \in V_{G} \}.\)
Numerous graphs have been studied in the past through M-Polynomial [17-19] and neighborhood M-polynomial [20].
Here represented some induced neighborhood degree dependent topological indices through NM-polynomial in Table 1.
| \(ND_{1}[G]\) =\(D_{u}^{\frac{1}{2}}D_{v}^{\frac{1}{2}}NM[G:u,v]|_{u=v=1}\) |
|---|
| \(ND_{2}[G]\) =\(S_{u}^{\frac{1}{2}} JNM[G:u,v]|_{u=1}\) |
| \(ND_{3}[G]\) =\(D_{u}D_{v}(D_{u} + D_{v})NM[G:u,v]|_{u=v=1}\) |
| \(ND_{4}[G]\) =\(S_{u}^{\frac{1}{2}}S_{v}^{\frac{1}{2}}NM_{G}(u,v)|_{u=v=1}\) |
| \(ND_{5}[G]\) =\((D_{u}S_{v} + S_{u}D_{v})NM[G:u,v]|_{u=v=1}\) |
| \(M_{1}^{'}[G]\) =\((D_{u}+D_{v})NM[G:u,v]|_{u=v=1}\) |
| \(M_{2}^{\maltese}[G]\) =\(D_{u}D_{v}NM[G:u,v]|_{u=v=1}\) |
| \(M_{2}^{nm}[G]\) =\(S_{u}S_{v}NM[G:u,v]|_{u=v=1}\) |
| \(F_{N}^{\maltese}[G]\) =\((D_{u}^{2}+D_{v}^{2})NM[G:u,v]|_{u=v=1}\) |
| \(NR_{\alpha}[G]\) =\(D_{u}^{\alpha}D_{v}^{\alpha}NM[G:u,v]|_{u=v=1}\) |
| \(NH[G]\) =\(2S_{u}JNM[G:u,v]|_{u=1}\) |
| \(NI[G]\) =\(S_{u}JD_{u}D_{v}NM[G:u,v]|_{u=1}\) |
| \(ABC_{4}[G]\) =\(D_{u}^{\frac{1}{2}}Q_{u(-2)}JS_{u}^{\frac{1}{2}}S_{v}^{\frac{1}{2}}NM[G:u,v]|_{u=1}\) |
| \(GA_{5}[G]\) =\(2S_{u}JD_{u}^{\frac{1}{2}}D_{v}^{\frac{1}{2}}NM[G:u,v]|_{u=1}\) |
| \(AG_{5}[G]\) =\(\frac{1}{2}S_{u}^{\frac{1}{2}}S_{v}^{\frac{1}{2}}(D_{u}+D_{v})NM[G:u,v]|_{u=v=1}\) |
| \(HM_{1}G_{5}[G]\) =\(D_{u}^{2}JNM[G:u,v]|_{u=1}\) |
| \(HM_{2}G_{5}[G]\) =\(D_{u}^{2}D_{v}^{2}NM[G:u,v]|_{u=v=1}\) |
| \(S[G]\) =\(S_{x}^{3}Q_{x(-2)}JD_{u}^{3}D_{v}^{3}NM[G:u,v]|_{u=1}\) |
Some operator which are used in Table 1 are defined in Table 2.
| \(D_{u}NM[G:u,v]\)=\(u\frac{\partial }{\partial u}NM[G:u,v],\) |
|---|
| \(D_{v}NM[G:u,v]\)=\(v\frac{\partial }{\partial v}NM[G:u,v],\) |
| \(D_{u}^{\frac{1}{2}}NM[G:u,v]\)=\(\sqrt{u\frac{\partial}{\partial u}NM[G:u,v]}\cdot \sqrt{NM[G:u,v]},\) |
| \(D_{v}^{\frac{1}{2}}NM[G:u,v]\)=\(\sqrt{v\frac{\partial}{\partial v}NM[G:u,v]}\cdot \sqrt{NM[G:u,v]},\) |
| \(S_{u}^{\frac{1}{2}}NM[G:u,v]\)=\(\sqrt{\int\limits_0^u\frac{NM[G:t,v]}{t}dt}\cdot \sqrt{NM[G:u,v]},\) |
| \(S_{v}^{\frac{1}{2}}NM[G:u,v]\)=\(\sqrt{\int\limits_0^v\frac{NM[G:u,t]}{t}dt} \cdot \sqrt{NM[G:u,v]},\) |
| \(JNM[G:u,v]\)=\(NM[G:u,v],\) |
| \(Q_{u(\alpha)}NM[G:u,v]\)=\(u^{\alpha}NM[G:u,v],\) |
| \(Q_{v(\alpha)}NM[G:u,v]\)=\(v^{\alpha}NM[G:u,v].\) |
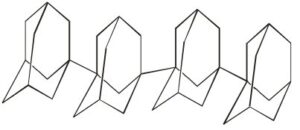
Diamondoids are known to be one of the most indispensable class of organic compounds due to their distinctive structural properties. These diamondoids are most powerful postulants for molecular building blocks (MBBs) to construct different nanostructures with over 20,000 permutations. The basic unit of diamondoids is adamantane which is tricyclic isomer \((C_{10}H_{16})\). Tetrameric 1-3 adamantane is very important isomer of this group of hydrocarbons.
This structure is studies by many researchers among the past [21,22]. In this chapter we discuss the molecular graphical structure of family of tetrameric 1-3 adamantane denoted by \(TA_n\). The numerical parameters such as neighbourhood degree based topological indices of \(TA_n\) are here to be computed by both direct and induced formulas via NM-polynomial. A tetrameric 1-n adamantane \(TA_n\) is shown in Figure 1 and the edge partition is shown in 3. The Table 3 is elaborated in terms of neighborhood degree of the vertices of graph.
| \((d_x,d_y)\) | Number of edges |
|---|---|
| (6,6) | \(2n+4\) |
| (6,7) | \(4n-1\) |
| (7,10) | \(4n-1\) |
| (8,10) | \(2n-2\) |
| (10,10) | \(n-1\) |
| Total edges | \(11n-1\) |
In this section we are about to compute NM-polynomial of \(TA_n\).
Theorem 1. If tetrameric 1-n adamantane is denoted by \(TA_n\) then for \(g\),\(h\),\(l \geq\) 3, NM-polynomial of \(TA_n\) is \(NM[TA_n:u,v]= (2n+4)u^{6}v^{6} +(4n-1)u^{6}v^{7} +(4n-1)u^{7}v^{10} +2(n-1)u^{8}v^{10} +(n-1)u^{10}v^{10}.\)
Proof. Let \(TA_n\) represented the tetrameric 1-n adamantane then by using Figure 1 and Table 3 we have the following edge partition of \(TA_n\)
\[\begin{aligned} &E_{6,6}(TA_n)= \{ e = xy \in E(TA_n)\ : Nd_{x} = 6, Nd_{y} = 6 \},\\ &|E_{6,6}TA_n|= 2n+4,\\ &E_{6,7}(TA_n)= \{ e = xy \in E(TA_n)\ : Nd_{x} = 6, Nd_{y} = 7 \}, \\ &|E_{6,7}TA_n|= 4n-1,\\ &E_{7,10}(TA_n)= \{ e = xy \in E(TA_n)\ : Nd_{x} = 7, Nd_{y} = 10 \}, \\ &|E_{7,10}TA_n|= 4n-1,\\ &E_{8,10}(TA_n)=\{ e = xy \in E(TA_n)\ : Nd_{x} = 8, Nd_{y} = 10 \}, \\ &|E_{8,10}TA_n|=2n-2,\\ &E_{10,10}(TA_n)=\{ e = xy \in E(TA_n)\ : Nd_{x} = 10,Nd_{y} = 10 \}, \\ &|E_{10,10}TA_n|=n-1. \end{aligned}\] The following result obtained by using the definition of NM-polynomial
\[\begin{aligned} NM[TA_n:u,v]= & \sum\limits_{\delta\leq i \leq j \leq \Delta} m_{i,j}(TA_n)u^{i}v^{j}\\ =& \sum\limits_{6 \leq i \leq j \leq 10} m_{i,j}(TA_n)u^{i}v^{j}\\ =& \sum\limits_{6 \leq 6} m_{6,6}(TA_n)u^{6}v^{6}\\ &+ \sum\limits_{6 \leq 7} m_{6,7}(TA_n)u^{6}v^{7} \\ &+ \sum\limits_{7 \leq 10} m_{7,10}(TA_n)u^{7}v^{10} \\ &+ \sum\limits_{8 \leq 10} m_{7,10}(TA_n)u^{7}v^{10}\\ &+ \sum\limits_{10 \leq 10} m_{10,10}(TA_n)u^{10}v^{10}\\ =& |E_{6,6}|u^{6}v^{6} + |E_{6,7}|u^{6}v^{7}\\ &+ |E_{7,10}|u^{7}v^{10} + |E_{8,10}|u^{8}v^{10} \\ &+ |E_{10,10}|u^{10}v^{10}\\ =& (2n+4)u^{6}v^{6} +(4n-1)u^{6}v^{7} \\ &+(4n-1)u^{7}v^{10} +2(n-1)u^{8}v^{10}\\ &+(n-1)u^{10}v^{10}. \end{aligned}\] ◻
In this section, we calculate few topological indices via NM-polynomial, computed in section 5, of \(TA_n\).
Theorem 2. Let \(TA_n\) be a tetrameric 1-n adamantane and \(NM[TA_n:u,v]=(2n+4)u^{6}v^{6} +(4n-1)u^{6}v^{7} +(4n-1)u^{7}v^{10} +2(n-1)u^{8}v^{10} +(n-1)u^{10}v^{10}.\) Then
\(ND_{1}(TA_n) = (22+\sqrt{42}+4\sqrt{70}+8\sqrt{5})n + (14-\sqrt{42}-\sqrt{70}-8\sqrt{5}).\)
\(ND_{2}(TA_n) = (\frac{\sqrt{12}}{6} + \frac{4\sqrt{13}}{13} + \frac{4\sqrt{17}}{17} + \frac{\sqrt{2}}{3} + \frac{\sqrt{20}}{20})n + (\frac{\sqrt{12}}{3} – \frac{\sqrt{13}}{13} – \frac{\sqrt{17}}{17} – \frac{\sqrt{2}}{3} + \frac{\sqrt{20}}{20}).\)
\(ND_{3}(TA_n) = 1586n-610.\)
\(ND_{4}(TA_n) = (\frac{13}{30} + \frac{2\sqrt{42}}{21} + \frac{2\sqrt{70}}{35} + \frac{\sqrt{5}}{10})n + (\frac{17}{30} – \frac{\sqrt{42}}{42} – \frac{\sqrt{70}}{70} – \frac{\sqrt{5}}{10}).\)
\(ND_{5}(TA_n) = \frac{2374}{105}n-\frac{3311}{1470}.\)
\(M_{1}^{'}(TA_n) = 200n-19.\)
\(M_{2}^{\maltese}(TA_n)= 780n-228.\)
\(M_{2}^{nm}(TA_n) = \frac{3061}{1260}n-\frac{827}{40320}.\)
\(F_{N}^{\maltese}(TA_n)= 1608n-474.\)
\(NR_{\alpha}(TA_n) = (2 \cdot 36^{\alpha} + 4 \cdot 42^{\alpha} + 4 \cdot 70^{\alpha} + 2 \cdot 80^{\alpha} + 100^{\alpha} )n + (4 \cdot 36^{\alpha} – 42^{\alpha} – 70^{\alpha} – 2 \cdot 80^{\alpha} – 100^{\alpha} ).\)
\(NH(TA_n) = \frac{34639}{19890}n + \frac{1451}{19890}.\)
\(NI(TA_n) = \frac{98023}{1989}n-\frac{18373}{1989}.\)
\(ABC_{4}(TA_n) = (\frac{\sqrt{10}}{3} + \frac{2\sqrt{462}}{21} + \frac{2\sqrt{72}}{7} + \frac{2\sqrt{5}}{5} + \frac{\sqrt{18}}{10})n + (\frac{2\sqrt{10}}{3} – \frac{\sqrt{462}}{42} – \frac{\sqrt{42}}{14} – \frac{2\sqrt{5}}{5} – \frac{\sqrt{18}}{10}).\)
\(GA_{5}(TA_n) = (3 + \frac{8\sqrt{42}}{13} + \frac{8\sqrt{70}}{17} + \frac{2\sqrt{5}}{9} )n + (3 – \frac{2\sqrt{42}}{13} – \frac{2\sqrt{70}}{17} – \frac{2\sqrt{5}}{9}).\)
\(AG_{5}(TA_n) = (3 + \frac{13\sqrt{42}}{21} + \frac{9\sqrt{5}}{10} + \frac{17\sqrt{70}}{35} )n + (3 – \frac{13\sqrt{42}}{84} – \frac{9\sqrt{5}}{10} – \frac{17\sqrt{70}}{140}).\)
\(HM_{1}G_{5}(TA_n) = 3168n-930.\)
\(HM_{2}G_{5}(TA_n) = 52048n-24280.\)
\(S(TA_n) = \frac{138746926286}{121287375}n – \frac{24926108606}{121287375}.\)
Proof. Let \(NM[TA_n:u,v]= (2n+4)u^{6}v^{6} +(4n-1)u^{6}v^{7} +(4n-1)u^{7}v^{10} +2(n-1)u^{8}v^{10} +(n-1)u^{10}v^{10}.\)
First \(NDe\) index
\(D_{v}^{\frac{1}{2}}NM[TA_n:u,v]=\sqrt{6}(2n+4)u^{6}v^{6} +\sqrt{7}(4n-1)u^{6}v^{7} +\sqrt{10}(4n-1)u^{7}v^{10} +2\sqrt{10}(n-1)u^{8}v^{10} +\sqrt{10}(n-1)u^{10}v^{10},\)
\(D_{u}^{\frac{1}{2}}D_{v}^{\frac{1}{2}}NM[TA_n:u,v]=6(2n+4)u^{6}v^{6} +\sqrt{42}(4n-1)u^{6}v^{7} +\sqrt{70}(4n-1)u^{7}v^{10} +8\sqrt{5}(n-1)u^{8}v^{10} +10(n-1)u^{10}v^{10},\)
\(ND_{1}(TA_n) =D_{u}^{\frac{1}{2}}D_{v}^{\frac{1}{2}}NM[TA_n:u,v]|_{u=v=1},\)
\(ND_{1}(TA_n) = (22+\sqrt{42}+4\sqrt{70}+8\sqrt{5})n + (14-\sqrt{42}-\sqrt{70}-8\sqrt{5}).\)
Second \(NDe\) index
\(JNM[TA_n:u,v]=(2n+4)u^{12} +(4n-1)u^{13} +(4n-1)u^{17} +2(n-1)u^{18} +(n-1)u^{20},\)
\(S_{u}^{\frac{1}{2}}JNM[TA_n:u,v]=\frac{\sqrt{12}}{6}(2n+4)u^{12} +\frac{1}{\sqrt{13}}(4n-1)u^{13} +\frac{1}{\sqrt{17}}(4n-1)u^{17} +\frac{\sqrt{2}}{3}(n-1)u^{18} +\frac{\sqrt{5}}{10}(n-1)u^{20},\)
\(ND_{2}[TA_n] =S_{u}^{\frac{1}{2}}JNM[TA_n:u,v]|_{u=1},\)
\(ND_{2}[TA_n] =(\frac{\sqrt{12}}{6} + \frac{4\sqrt{13}}{13} + \frac{4\sqrt{17}}{17} + \frac{\sqrt{2}}{3} + \frac{\sqrt{20}}{20})n + (\frac{\sqrt{12}}{3} – \frac{\sqrt{13}}{13} – \frac{\sqrt{17}}{17} – \frac{\sqrt{2}}{3} + \frac{\sqrt{20}}{20}).\)
Third \(NDe\) index
\(D_{v}NM[TA_n:u,v]=6(2n+4)u^{6}v^{6} +7(4n-1)u^{6}v^{7} +10(4n-1)u^{7}v^{10} +20(n-1)u^{8}v^{10} +10(n-1)u^{10}v^{10},\)
\(D_{u}NM[TA_n:u,v]=6(2n+4)u^{6}v^{6} +6(4n-1)u^{6}v^{7} +7(4n-1)u^{7}v^{10}+16(n-1)u^{8}v^{10} +10(n-1)u^{10}v^{10},\)
\((D_{u} + D_{v})NM[TA_n:u,v]=12(2n+4)u^{6}v^{6}+13(4n-1)u^{6}v^{7}+17(4n-1)u^{7}v^{10} +36(n-1)u^{8}v^{10} +20(n-1)u^{10}v^{10},\)
\(D_{v}(D_{u} + D_{v})NM[TA_n:u,v]=72(2n+4)u^{6}v^{6}+91(4n-1)u^{6}v^{7}+170(4n-1)u^{7}v^{10} +360(n-1)u^{8}v^{10} +200(n-1)u^{10}v^{10},\)
\(D_{u}D_{v}(D_{u} + D_{v})NM[TA_n:u,v]=432(2n+4)u^{6}v^{6}+546(4n-1)u^{6}v^{7}+1190(4n-1)u^{7}v^{10} +1440(n-1)u^{8}v^{10} +2000(n-1)u^{10}v^{10},\)
\(ND_{3}[TA_n] =D_{u}D_{v}(D_{u} + D_{v})NM[TA_n:u,v]|_{u=v=1},\)
\(ND_{3}[TA_n] =1586n-610.\)
Fourth \(NDe\) index
\(S_{v}^{\frac{1}{2}}NM[TA_n:u,v]=\frac{\sqrt{6}}{6}(2n+4)u^{6}v^{6} +\frac{\sqrt{7}}{7}(4n-1)u^{6}v^{7} +\frac{\sqrt{10}}{10}(4n-1)u^{7}v^{10}+\frac{\sqrt{10}}{5}(n-1)u^{8}v^{10} +\frac{\sqrt{10}}{10}(n-1)u^{10}v^{10},\)
\(S_{u}^{\frac{1}{2}}S_{v}^{\frac{1}{2}}NM[TA_n:u,v]=\frac{1}{6}(2n+4)u^{6}v^{6} +\frac{\sqrt{42}}{42}(4n-1)u^{6}v^{7} +\frac{\sqrt{70}}{70}(4n-1)u^{7}v^{10} +\frac{\sqrt{5}}{20}(n-1)u^{8}v^{10} +\frac{1}{100}(n-1)u^{10}v^{10},\)
\(ND_{4}[TA_n] =S_{u}^{\frac{1}{2}}S_{v}^{\frac{1}{2}}NM[TA_n:u,v]|_{u=v=1},\)
\(ND_{4}[TA_n] =(\frac{13}{30} + \frac{2\sqrt{42}}{21} + \frac{2\sqrt{70}}{35} + \frac{\sqrt{5}}{10})n + (\frac{17}{30} – \frac{\sqrt{42}}{42} – \frac{\sqrt{70}}{70} – \frac{\sqrt{5}}{10}).\)
Fifth \(NDe\) index
\(D_{v}NM[TA_n:u,v]=6(2n+4)u^{6}v^{6} +7(4n-1)u^{6}v^{7} +10(4n-1)u^{7}v^{10} +20(n-1)u^{8}v^{10} +10(n-1)u^{10}v^{10},\)
\(S_{u}D_{v}NM[TA_n:u,v]=(2n+4)u^{6}v^{6} +\frac{7}{6}(4n-1)u^{6}v^{7} +\frac{10}{7}(4n-1)u^{7}v^{10}\ +\frac{5}{2}(n-1)u^{8}v^{10} +(n-1)u^{10}v^{10},\)
\(S_{v}NM[TA_n:u,v]=\frac{1}{6}(2n+4)u^{6}v^{6} +\frac{1}{7}(4n-1)u^{6}v^{7} +\frac{1}{10}(4n-1)u^{7}v^{10} +\frac{1}{5}(n-1)u^{8}v^{10} +\frac{1}{10}(n-1)u^{10}v^{10},\)
\(D_{u}S_{v}NM[TA_n:u,v]=(2n+4)u^{6}v^{6} +\frac{6}{7}(4n-1)u^{6}v^{7} +\frac{7}{10}(4n-1)u^{7}v^{10} +\frac{8}{5}(n-1)u^{8}v^{10} +(n-1)u^{10}v^{10},\)
\((D_{u}S_{v} + S_{u}D_{v})NM[TA_n:u,v]=2(2n+4)u^{6}v^{6} +\frac{85}{42}(4n-1)u^{6}v^{7} +\frac{149}{70}(4n-1)u^{7}v^{10} +\frac{164}{40}(n-1)u^{8}v^{10} +2(n-1)u^{10}v^{10},\)
\(ND_{5}[TA_n] =(D_{u}S_{v} + S_{u}D_{v})NM[TA_n:u,v]|_{u=v=1},\)
\(ND_{5}[TA_n] =\frac{2374}{105}n-\frac{3311}{1470}.\)
Third version of Zagreb index
\(D_{u}NM[TA_n:u,v]=6(2n+4)u^{6}v^{6} +6(4n-1)u^{6}v^{7} +7(4n-1)u^{7}v^{10} +16(n-1)u^{8}v^{10} +10(n-1)u^{10}v^{10},\)
\(D_{v}NM[TA_n:u,v]=6(2n+4)u^{6}v^{6} +7(4n-1)u^{6}v^{7} +10(4n-1)u^{7}v^{10} +20(n-1)u^{8}v^{10} +10(n-1)u^{10}v^{10},\)
\((D_{u}+D_{v})NM[TA_n:u,v]=12(2n+4)u^{6}v^{6}+13(4n-1)u^{6}v^{7}+17(4n-1)u^{7}v^{10} +36(n-1)u^{8}v^{10} +20(n-1)u^{10}v^{10},\)
\(M_{1}^{'}[TA_n] =(D_{u}+D_{v})NM[TA_n:u,v]|_{u=v=1},\)
\(M_{1}^{'}[TA_n] =200n-19.\)
Neighborhood second Zagreb index
\(D_{v}NM[TA_n:u,v]=6(2n+4)u^{6}v^{6} +7(4n-1)u^{6}v^{7} +10(4n-1)u^{7}v^{10} +20(n-1)u^{8}v^{10} +10(n-1)u^{10}v^{10},\)
\(D_{u}D_{v}NM[TA_n:u,v]=36(2n+4)u^{6}v^{6} +42(4n-1)u^{6}v^{7} +70(4n-1)u^{7}v^{10} +160(n-1)u^{8}v^{10} +100(n-1)u^{10}v^{10},\)
\(M_{2}^{\maltese}[TA_n] =D_{u}D_{v}NM[TA_n:u,v]|_{u=v=1},\)
\(M_{2}^{\maltese}[TA_n] =780n-228.\)
Neighborhood second modified Zagreb index
\(S_{v}NM[TA_n:u,v]=\frac{1}{6}(2n+4)u^{6}v^{6} +\frac{1}{7}(4n-1)u^{6}v^{7} +\frac{1}{10}(4n-1)u^{7}v^{10}+\frac{1}{5}(n-1)u^{8}v^{10} +\frac{1}{10}(n-1)u^{10}v^{10},\)
\(S_{u}S_{v}NM[TA_n:u,v]=\frac{1}{36}(2n+4)u^{6}v^{6} +\frac{1}{42}(4n-1)u^{6}v^{7} +\frac{1}{70}(4n-1)u^{7}v^{10} +\frac{1}{40}(n-1)u^{8}v^{10} +\frac{1}{100}(n-1)u^{10}v^{10},\)
\(M_{2}^{nm}[TA_n] =S_{u}S_{v}NM[TA_n:u,v]|_{u=v=1},\)
\(M_{2}^{nm}[TA_n] =\frac{3061}{1260}n-\frac{827}{40320}.\)
Neighborhood forgotten topological index
\(D_{u}^{2}NM[TA_n:u,v]=36(2n+4)u^{6}v^{6} +36(4n-1)u^{6}v^{7} +49(4n-1)u^{7}v^{10}+128(n-1)u^{8}v^{10} +100(n-1)u^{10}v^{10},\)
\(D_{v}^{2}NM[TA_n:u,v]=36(2n+4)u^{6}v^{6} +49(4n-1)u^{6}v^{7} +100(4n-1)u^{7}v^{10} +200(n-1)u^{8}v^{10} +100(n-1)u^{10}v^{10},\)
\((D_{u}^{2}+D_{v}^{2})NM[TA_n:u,v]=72(2n+4)u^{6}v^{6} +85(4n-1)u^{6}v^{7} +149(4n-1)u^{7}v^{10} +328(n-1)u^{8}v^{10} +200(n-1)u^{10}v^{10},\)
\(F_{N}^{\maltese}[TA_n] =(D_{u}^{2}+D_{v}^{2})NM[TA_n:u,v]|_{u=v=1},\)
\(F_{N}^{\maltese}[TA_n] =1608n-474.\)
Neighborhood general Randić index
\(D_{v}^{\alpha}NM[TA_n:u,v]=6^{\alpha}(2n+4)u^{6}v^{6} +7^{\alpha}(4n-1)u^{6}v^{7} +10^{\alpha}(4n-1)u^{7}v^{10} +2 \cdot 10^{\alpha}(n-1)u^{8}v^{10} +10^{\alpha}(n-1)u^{10}v^{10},\)
\(D_{u}^{\alpha}D_{v}^{\alpha}NM[TA_n:u,v]=36^{\alpha}(2n+4)u^{6}v^{6} +42^{\alpha}(4n-1)u^{6}v^{7} +70^{\alpha}(4n-1)u^{7}v^{10} +2 \cdot 80^{\alpha}(n-1)u^{8}v^{10} +100^{\alpha}(n-1)u^{10}v^{10},\)
\(NR_{\alpha}[TA_n] =D_{u}^{\alpha}D_{v}^{\alpha}NM[TA_n:u,v]|_{u=v=1},\)
\(NR_{\alpha}[TA_n] =(2 \cdot 36^{\alpha} + 4 \cdot 42^{\alpha} + 4 \cdot 70^{\alpha} + 2 \cdot 80^{\alpha} + 100^{\alpha} )n + (4 \cdot 36^{\alpha} – 42^{\alpha} – 70^{\alpha} – 2 \cdot 80^{\alpha} – 100^{\alpha} ).\)
Neighborhood harmonic index
\(JNM[TA_n:u,v]=(2n+4)u^{12} +(4n-1)u^{13} +(4n-1)u^{17} +2(n-1)u^{18} +(n-1)u^{20},\)
\(S_{u}JNM[TA_n:u,v]=\frac{1}{12}(2n+4)u^{12} +\frac{1}{13}(4n-1)u^{13} +\frac{1}{17}(4n-1)u^{17} +\frac{1}{9}(n-1)u^{18} +\frac{1}{20}(n-1)u^{20},\)
\(2S_{u}JNM[TA_n:u,v]=\frac{1}{6}(2n+4)u^{12} +\frac{2}{13}(4n-1)u^{13} +\frac{2}{17}(4n-1)u^{17} +\frac{2}{9}(n-1)u^{18} +\frac{1}{10}(n-1)u^{20},\)
\(NH[TA_n] =2S_{u}JNM[TA_n:u,v]|_{u=1},\)
\(NH[TA_n] =\frac{34639}{19890}n + \frac{1451}{19890}.\)
Neighborhood inverse sum index
\(D_{v}NM[TA_n:u,v]=6(2n+4)u^{6}v^{6} +7(4n-1)u^{6}v^{7} +10(4n-1)u^{7}v^{10} +20(n-1)u^{8}v^{10} +10(n-1)u^{10}v^{10},\)
\(D_{u}D_{v}NM[TA_n:u,v]=36(2n+4)u^{6}v^{6} +42(4n-1)u^{6}v^{7} +70(4n-1)u^{7}v^{10} +160(n-1)u^{8}v^{10} +100(n-1)u^{10}v^{10},\)
\(JD_{u}D_{v}NM[TA_n:u,v]=36(2n+4)u^{12} +42(4n-1)u^{13} +70(4n-1)u^{17} +160(n-1)u^{18} +100(n-1)u^{20},\)
\(S_{u}JD_{u}D_{v}NM[TA_n:u,v]=3(2n+4)u^{12} +\frac{42}{13}(4n-1)u^{13} +\frac{70}{17}(4n-1)u^{17} +\frac{80}{9}(n-1)u^{18} +5(n-1)u^{20},\)
\(NI[TA_n] =S_{u}JD_{u}D_{v}NM[TA_n:u,v]|_{u=1},\)
\(NI[TA_n] =\frac{98023}{1989}n-\frac{18373}{1989}.\)
Fourth atom bond connectivity index
\(S_{v}^{\frac{1}{2}}NM[TA_n:u,v]=\frac{\sqrt{6}}{6}(2n+4)u^{6}v^{6} +\frac{\sqrt{7}}{7}(4n-1)u^{6}v^{7} +\frac{\sqrt{10}}{10}(4n-1)u^{7}v^{10} +\frac{\sqrt{10}}{5}(n-1)u^{8}v^{10} +\frac{\sqrt{10}}{10}(n-1)u^{10}v^{10},\)
\(S_{u}^{\frac{1}{2}}S_{v}^{\frac{1}{2}}NM[TA_n:u,v]=\frac{1}{6}(2n+4)u^{6}v^{6} +\frac{\sqrt{42}}{42}(4n-1)u^{6}v^{7} +\frac{\sqrt{70}}{70}(4n-1)u^{7}v^{10} +\frac{\sqrt{5}}{20}(n-1)u^{8}v^{10} +\frac{}{100}(n-1)u^{10}v^{10},\)
\(JS_{u}^{\frac{1}{2}}S_{v}^{\frac{1}{2}}NM[TA_n:u,v]=\frac{1}{6}(2n+4)u^{12} +\frac{\sqrt{42}}{42}(4n-1)u^{13} +\frac{\sqrt{70}}{70}(4n-1)u^{17} +\frac{\sqrt{5}}{20}(n-1)u^{18} +\frac{1}{100}(n-1)u^{20},\)
\(Q_{u(-2)}JS_{u}^{\frac{1}{2}}S_{v}^{\frac{1}{2}}NM[TA_n:u,v]=\frac{1}{6}(2n+4)u^{10} +\frac{\sqrt{42}}{42}(4n-1)u^{11} +\frac{\sqrt{70}}{70}(4n-1)u^{15}\ +\frac{\sqrt{5}}{20}(n-1)u^{16} +\frac{1}{100}(n-1)u^{18},\)
\(D_{u}^{\frac{1}{2}}Q_{u(-2)}JS_{u}^{\frac{1}{2}}S_{v}^{\frac{1}{2}}NM[TA_n:u,v]=\frac{\sqrt{10}}{6}(2n+4)u^{10} +\frac{\sqrt{462}}{42}(4n-1)u^{11} +\frac{\sqrt{42}}{14}(4n-1)u^{15} +\frac{\sqrt{5}}{5}(n-1)u^{16} +\frac{1}{100}(n-1)u^{18},\)
\(ABC_{4}[TA_n] =D_{u}^{\frac{1}{2}}Q_{u(-2)}JS_{u}^{\frac{1}{2}}S_{v}^{\frac{1}{2}}NM[TA_n:u,v]|_{u=1}\)
\(ABC_{4}[TA_n] = (\frac{\sqrt{10}}{3} + \frac{2\sqrt{462}}{21} + \frac{2\sqrt{72}}{7} + \frac{2\sqrt{5}}{5} + \frac{\sqrt{18}}{10})n + (\frac{2\sqrt{10}}{3} – \frac{\sqrt{462}}{42} – \frac{\sqrt{42}}{14} – \frac{2\sqrt{5}}{5} – \frac{\sqrt{18}}{10}).\)
Fifth geometric arithmetics index
\(D_{v}^{\frac{1}{2}}NM[TA_n:u,v]=\sqrt{6}(2n+4)u^{6}v^{6} +\sqrt{7}(4n-1)u^{6}v^{7} +\sqrt{10}(4n-1)u^{7}v^{10} +2\sqrt{10}(n-1)u^{8}v^{10} +\sqrt{10}(n-1)u^{10}v^{10},\)
\(D_{u}^{\frac{1}{2}}D_{v}^{\frac{1}{2}}NM[TA_n:u,v]=6(2n+4)u^{6}v^{6} +\sqrt{42}(4n-1)u^{6}v^{7} +\sqrt{70}(4n-1)u^{7}v^{10} +8\sqrt{5}(n-1)u^{8}v^{10} +10(n-1)u^{10}v^{10},\)
\(JD_{u}^{\frac{1}{2}}D_{v}^{\frac{1}{2}}NM[TA_n:u,v]=6(2n+4)u^{12} +\sqrt{42}(4n-1)u^{13} +\sqrt{70}(4n-1)u^{17} +8\sqrt{5}(n-1)u^{18} +10(n-1)u^{20},\)
\(S_{u}JD_{u}^{\frac{1}{2}}D_{v}^{\frac{1}{2}}NM[TA_n:u,v]=\frac{1}{2}(2n+4)u^{12} +\frac{\sqrt{42}}{13}(4n-1)u^{13} +\frac{\sqrt{70}}{17}(4n-1)u^{17} +\frac{4\sqrt{5}}{9}(n-1)u^{18} +\frac{1}{2}(n-1)u^{20},\)
\(2S_{u}JD_{u}^{\frac{1}{2}}D_{v}^{\frac{1}{2}}NM[TA_n:u,v]=(2n+4)u^{12} +\frac{2\sqrt{42}}{13}(4n-1)u^{13} +\frac{2\sqrt{70}}{17}(4n-1)u^{17} +\frac{8\sqrt{5}}{9}(n-1)u^{18} +(n-1)u^{20},\)
\(GA_{5}[TA_n] =2S_{u}JD_{u}^{\frac{1}{2}}D_{v}^{\frac{1}{2}}NM[TA_n:u,v]|_{u=1},\)
\(GA_{5}[TA_n] = (3 + \frac{8\sqrt{42}}{13} + \frac{8\sqrt{70}}{17} + \frac{2\sqrt{5}}{9} )n + (3 – \frac{2\sqrt{42}}{13} – \frac{2\sqrt{70}}{17} – \frac{2\sqrt{5}}{9}).\)
Fifth arithmetics geometric index
\(D_{u}NM[TA_n:u,v]=6(2n+4)u^{6}v^{6} +6(4n-1)u^{6}v^{7} +7(4n-1)u^{7}v^{10} +16(n-1)u^{8}v^{10} +10(n-1)u^{10}v^{10},\)
\(D_{v}NM[TA_n:u,v]=6(2n+4)u^{6}v^{6} +7(4n-1)u^{6}v^{7} +10(4n-1)u^{7}v^{10} +20(n-1)u^{8}v^{10} +10(n-1)u^{10}v^{10},\)
\((D_{u}+D_{v})NM[TA_n:u,v]=12(2n+4)u^{6}v^{6}+13(4n-1)u^{6}v^{7}+17(4n-1)u^{7}v^{10} +36(n-1)u^{8}v^{10} +20(n-1)u^{10}v^{10},\)
\(S_{v}^{\frac{1}{2}}(D_{u}+D_{v})NM[TA_n:u,v]=2\sqrt{6}(2n+4)u^{6}v^{6}+\frac{13\sqrt{7}}{7}(4n-1)u^{6}v^{7}+\frac{17\sqrt{10}}{10}(4n-1)u^{7}v^{10} +\frac{18\sqrt{10}}{5}(n-1)u^{8}v^{10} +\frac{2\sqrt{10}}{5}(n-1)u^{10}v^{10},\)
\(S_{u}^{\frac{1}{2}}S_{v}^{\frac{1}{2}}(D_{u}+D_{v})NM[TA_n:u,v]=12(2n+4)u^{6}v^{6}+\frac{13\sqrt{42}}{42}(4n-1)u^{6}v^{7}+\frac{17\sqrt{70}}{70}(4n-1)u^{7}v^{10} +\frac{9\sqrt{5}}{5}(n-1)u^{8}v^{10} +4(n-1)u^{10}v^{10},\)
\(\frac{1}{2}S_{u}^{\frac{1}{2}}S_{v}^{\frac{1}{2}}(D_{u}+D_{v})NM[TA_n:u,v]=6(2n+4)u^{6}v^{6}+\frac{13\sqrt{42}}{84}(4n-1)u^{6}v^{7}+\frac{17\sqrt{70}}{140}(4n-1)u^{7}v^{10} +\frac{9\sqrt{5}}{10}(n-1)u^{8}v^{10} +2(n-1)u^{10}v^{10},\)
\(AG_{5}[TA_n] =\frac{1}{2}S_{u}^{\frac{1}{2}}S_{v}^{\frac{1}{2}}(D_{u}+D_{v})NM[TA_n:u,v]|_{u=v=1},\)
\(AG_{5}[TA_n] =(3 + \frac{13\sqrt{42}}{21} + \frac{9\sqrt{5}}{10} + \frac{17\sqrt{70}}{35} )n+ (3 – \frac{13\sqrt{42}}{84} – \frac{9\sqrt{5}}{10} – \frac{17\sqrt{70}}{140}).\)
Fifth hyper first Zagreb index
\(JNM[G:u,v]=(2n+4)u^{12} +(4n-1)u^{13} +(4n-1)u^{17} +2(n-1)u^{18} +(n-1)u^{20},\)
\(D_{u}^{2}JNM[G:u,v]=144(2n+4)u^{12} +169(4n-1)u^{13} +289(4n-1)u^{17} +648(n-1)u^{18} +400(n-1)u^{20},\)
\(HM_{1}G_{5}[TA_n] =D_{u}^{2}JNM[G:u,v]|_{u=1},\)
\(HM_{1}G_{5}[TA_n] = 3168n-930.\)
Fifth hyper second Zagreb index
\(D_{v}^{2}NM[G:u,v]=36(2n+4)u^{6}v^{6} +49(4n-1)u^{6}v^{7} +100(4n-1)u^{7}v^{10} +200(n-1)u^{8}v^{10} +100(n-1)u^{10}v^{10},\)
\(D_{u}^{2}D_{v}^{2}NM[G:u,v]=1296(2n+4)u^{6}v^{6} +1764(4n-1)u^{6}v^{7} +4900(4n-1)u^{7}v^{10} +6400(n-1)u^{8}v^{10} +10000(n-1)u^{10}v^{10},\)
\(HM_{2}G_{5}[TA_n] =D_{u}^{2}D_{v}^{2}NM[G:u,v]|_{u=v=1},\)
\(HM_{2}G_{5}[TA_n] = 52048n-24280.\)
Sunskuti index
\(D_{v}^{3}NM[G:u,v]=216(2n+4)u^{6}v^{6} +343(4n-1)u^{6}v^{7} +1000(4n-1)u^{7}v^{10} +2000(n-1)u^{8}v^{10} +1000(n-1)u^{10}v^{10},\)
\(D_{u}^{3}D_{v}^{3}NM[G:u,v]=46656(2n+4)u^{6}v^{6} +74088(4n-1)u^{6}v^{7} +343000(4n-1)u^{7}v^{10} +512000(n-1)u^{8}v^{10} +1000000(n-1)u^{10}v^{10},\)
\(JD_{u}^{3}D_{v}^{3}NM[G:u,v]=46656(2n+4)u^{12} +74088(4n-1)u^{13} +343000(4n-1)u^{17} +512000(n-1)u^{18} +1000000(n-1)u^{20},\)
\(S_{x}^{3}Q_{x(-2)}JD_{u}^{3}D_{v}^{3}NM[G:u,v]=\frac{46656}{1000}(2n+4)u^{10} +\frac{74088}{1331}(4n-1)u^{11} +\frac{343000}{3375}(4n-1)u^{15} +\frac{512000}{4096}(n-1)u^{16} +\frac{1000000}{5832}(n-1)u^{18},\)
\(S[TA_n] =S_{x}^{3}Q_{x(-2)}JD_{u}^{3}D_{v}^{3}NM[G:u,v]|_{u=1},\)
\(S[TA_n]=\frac{138746926286}{121287375}n – \frac{24926108606}{121287375}.\)
◻
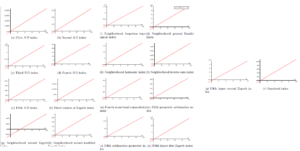
Figure 2 shows graphically representation of topological indices of \(TA_n\). From graphs, we see the behavior of the topological indices along different parameters. Despite the fact that the graphs are looking to be identical, but have distinct gradients.
This work comprises computations of general form of NM-polynomials and some neighborhood topological indices of tetrameric 1-3 adamanatane through induced formulas. We represented graphs for better envision of NM-polynomial and neighborhood topological indices. Our results will definitely contribute for the study of physio-chemical properties of these compounds. Due to its vast scope in chemistry, we will surely like to do comuptations of these invariants for some other chemical graphs.